Have you ever wondered about the different types of vowels in the English language? Well, in this article, I’ll delve into the fascinating world of vowels and explore the various types that exist. From long vowels to short vowels, we’ll uncover the intricacies of vowel sounds and their importance in language.
Vowels are an essential component of our speech, and understanding their different sounds can greatly enhance our communication skills. Whether you’re a language enthusiast, a student, or simply curious about the mechanics of language, this article will provide you with valuable insights.
Throughout this article, we’ll explore the seven types of syllables and the most common vowel sound in English, known as the schwa. We’ll also delve into the distinction between long vowels and short vowels, and provide examples to help you grasp the concept.
So, if you’re ready to embark on a journey through the world of vowels, let’s dive in and explore the fascinating nuances of these essential linguistic elements.
What Is A Vowel?
Vowels play a crucial role in the English language. Understanding what exactly constitutes a vowel is essential for effective communication. As an expert in language mechanics, I am here to provide you with a clear and concise explanation of what vowels are.
Technically, vowels are produced by releasing air from the lungs through the oral and/or nasal cavity. But what sets vowels apart from other sounds is their syllabic nature. Unlike consonants, vowels are capable of forming a syllable on their own.
It’s worth noting that some sounds, like the “W” in “with” or the “Y” in “year,” may resemble vowels, but they lack the vital characteristic of being syllabic. Therefore, they do not fall under the category of vowels.

In the English language, vowel sounds can be classified into several categories, including short vowels, long vowels, diphthongs, vowels before historical “R,” and weak vowels. Each category has its own distinctive characteristics and pronunciation patterns.
Without a doubt, vowels are the backbone of our oral expression. By understanding their nuances and mastering their sounds, we can communicate effectively and express ourselves with clarity and precision.
With this brief introduction to the concept of vowels, you can now embark on a journey through the fascinating world of vowel sounds. In the upcoming sections, we will explore the different types of vowels in more detail, providing you with examples and insights that will deepen your understanding of this integral aspect of the English language.
Stay tuned to learn more about short and long vowels, diphthongs, and the role of vowels before “R.” Get ready to unlock the secrets of vowel sounds and enhance your language skills. Let’s dive into this enriching exploration of the diverse and captivating world of vowels.
Vowel Letters
When it comes to vowels, we often think of them as individual letters in the English alphabet. And while it’s true that vowels are represented by specific letters, it’s important to understand that the relationship between vowel sounds and vowel letters is not always one-to-one.
In the English language, there are six vowel letters: A, E, I, O, U, and sometimes Y. These letters can represent a variety of vowel sounds depending on the word and its pronunciation. The letter Y is particularly interesting because it can function as both a vowel and a consonant, depending on the word and context.
Let’s explore some examples of vowel letters in common English words:
- Unit: In this word, the vowel letters are U and I.
- Chocolate: Here, the vowel letters are O, A, and E.
- Rainy: The vowel letters in this word are A, I, and Y.
As you can see, even though there are only five vowel letters in English, we actually have a lot more vowel sounds than that. Each vowel letter can be used to represent multiple vowel sounds, adding to the richness and complexity of the English language.
Understanding the relationship between vowel sounds and vowel letters is essential for effective communication. By mastering the different vowel sounds and their corresponding letters, you can enhance your pronunciation and fluency in English.
In the next sections, we will delve into each type of vowel in more detail, providing examples and insights to deepen your understanding. From short vowels to long vowels, diphthongs to weak vowels, we will explore the diverse and captivating world of vowels. So stay tuned for more in-depth knowledge on the types of vowels and how they contribute to clear and precise oral expression.
When Do You Need a Vowel?
When it comes to the English language, it is essential to understand the significance of vowels and when they are needed. Vowels play a crucial role in communication, spelling, grammar, and even in learning how to read and write. Let’s explore the various scenarios in which vowels are needed:
- Every Word Requires at Least One Vowel: Unlike consonants, every word in English needs to have at least one vowel. This rule applies to the majority of words, with only a few exceptions. So, whether you’re writing a short word like “a” or expressing your thoughts with a more complex word, vowels are indispensable for effective communication.
- Every Syllable Needs a Vowel Sound: In addition to each word requiring a vowel, every syllable also needs a vowel sound. If a word has more than one syllable, it will have more than one vowel. Understanding this concept is crucial for both reading and pronouncing words correctly.
- Creating Speech Sounds and Phonetics: The human mouth is naturally designed to produce vowel sounds, as they are an inherent part of our speech. We produce vowel sounds even when we laugh, cry, or speak in any language. Vowels are also essential for singing. Have you ever tried singing a consonant sound like “k” or “t”? It’s impossible! Vowels are necessary to sustain a sound for a long time, while consonants only last for a moment.
So, whether you’re writing, speaking, or singing, vowels are essential in expressing yourself clearly and effectively. The next sections of this article will delve deeper into the different types of vowel sounds in the English language, providing examples and insights to enhance your understanding.

20 Common Vowels With Examples
When it comes to understanding vowels, it’s crucial to familiarize ourselves with the different types of vowel sounds. In the English language, vowels can be classified into several categories, each with its own unique pronunciation. In this section, I’ll explore 20 common vowel sounds and provide examples to help deepen your understanding.
- The letter “A” is a versatile vowel that can make various sounds, such as in the words “cat,” “cake,” and “ball.”
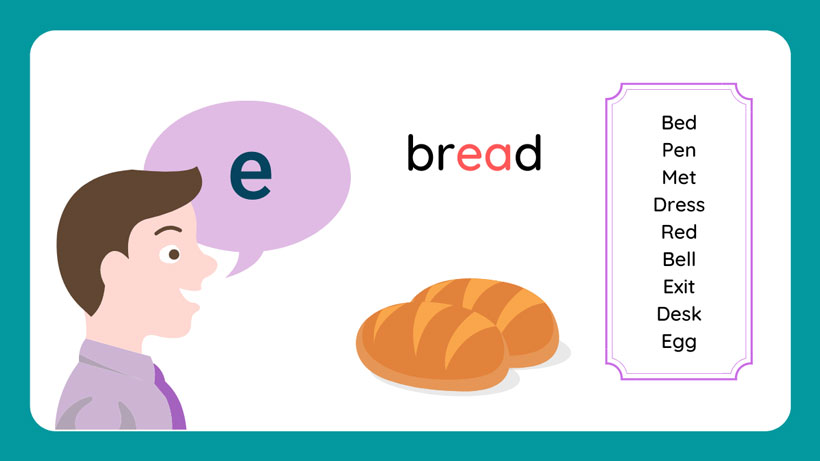
- “E” is another frequently used vowel, producing sounds like those in “bed,” “see,” and “red.”
- With “I,” you can hear its distinct sounds in words like “bit,” “time,” and “fight.”
- “O” contributes to the vowel sounds in words such as “dog,” “hope,” and “note.”
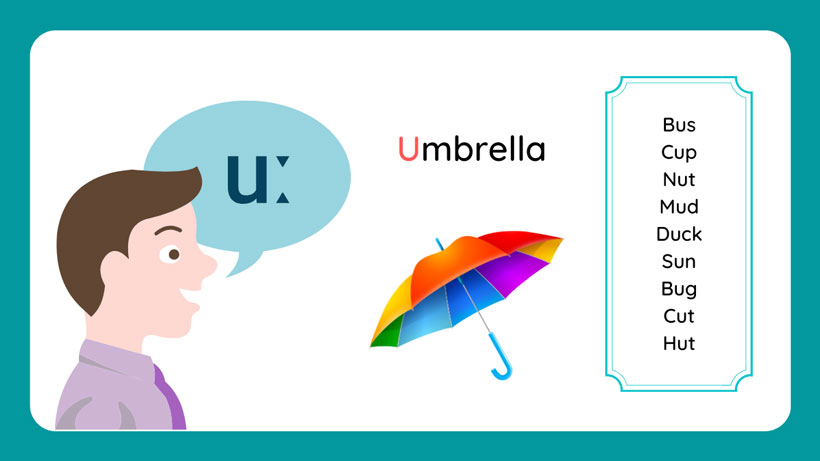
- “U” is responsible for producing sounds in words like “bus,” “tube,” and “mud.”
- Sometimes, the letter “Y” acts as a vowel, representing sounds like those in “fly,” “myth,” and “cycle.”
- Vowel combinations can also create unique sounds, such as “AI” in “rain,” “EA” in “seat,” and “OU” in “round.”
- Long vowel sounds are made with a prolonged pronunciation of the vowels, as heard in words like “game,” “road,” and “cute.”
- Short vowel sounds are short and crisp, like in words such as “cat,” “pet,” and “hit.”
- Diphthongs are combinations of two vowel sounds within a single syllable, as observed in words like “coin,” “loud,” and “boy.”
- Vowels before historical “R” can take on different sounds, like in “care,” “here,” and “fire.”
- Weak vowels often appear as reduced sounds in unstressed syllables, such as “butter,” “pencil,” and “rabbit.”
- The schwa sound, represented by a backwards “e” symbol (ə), occurs in unstressed syllables, as in the word “about” or “common.”
- “OY” creates a unique sound in words like “boy,” “toy,” and “enjoy.”

Types of Vowels
Monophthongs
Monophthongs are single, unchanging vowel sounds. When pronounced, they maintain a steady-state without gliding or transitioning into another sound. In English, there are several monophthongs that are represented by specific vowel letters. Here are some examples of monophthongs:
- The short “a” sound as in the word “cat”
- The long “a” sound as in the word “gate”
- The short “e” sound as in the word “bed”
- The long “e” sound as in the word “bee”
- The short “i” sound as in the word “pig”
- The long “i” sound as in the word “kite”
- The short “o” sound as in the word “hot”
- The long “o” sound as in the word “bone”
- The short “u” sound as in the word “cup”
- The long “u” sound as in the word “tube”
Diphthongs
Diphthongs are gliding vowels that consist of two vowel sounds or vowel letters blended together within the same syllable. The transition from one sound to another creates a unique diphthong sound. In English, there are various diphthongs that add richness and complexity to speech. Here are some examples of diphthongs:
- The “ai” sound as in the word “pain”
- The “ei” sound as in the word “eight”
- The “oi” sound as in the word “coin”
- The “au” sound as in the word “autumn”
- The “ou” sound as in the word “mouse”
- The “əʊ” sound as in the word “boat”
- The “aɪ” sound as in the word “sky”
- The “eɪ” sound as in the word “day”
- The “əʊ” sound as in the word “go”
- The “juː” sound as in the word “cute”
Understanding the distinctions between monophthongs and diphthongs is crucial for accurate pronunciation and effective communication in English. Mastering these vowel sounds will significantly enhance your ability to express yourself clearly and fluently.
Monophthongs
Definition:
Monophthongs are single vowel sounds that do not change or glide into another sound. Unlike diphthongs, which are a combination of two vowel sounds, monophthongs are stable and do not have a transition between different positions in the vocal tract.
Examples:
Here are some examples of monophthongs in English:
- “kit” – /ɪ/ (short “i” sound)
- “dress” – /ɛ/ (short “e” sound)
- “trap” – /æ/ (short “a” sound)
- “strut” – /ʌ/ (short “u” sound)
- “lot” – /ɒ/ (short “o” sound)
- “foot” – /ʊ/ (short “u” sound)
These monophthongs represent different vowel sounds in English words. Mastering these sounds is crucial for clear and accurate pronunciation, as well as effective communication. By understanding the distinct characteristics of each monophthong, you will be able to express yourself fluently and confidently in English.
Diphthongs
Definition
Diphthongs are a combination of two vowel sounds or vowel letters that come together within the same syllable. Unlike monophthongs, which are single vowel sounds that do not change or glide into another sound, diphthongs involve a continuous transition from one position to another in the articulation of the vowels. This creates a unique and distinctive sound that is essential to effective communication.
Examples
To understand diphthongs, it’s helpful to listen to how certain words sound when pronounced. Here are some examples of common diphthongs in the English language:
- “ai” as in “pipe” or “paɪp”
- “ou” as in “doubt”
In these examples, the vowel sounds transition smoothly from one position to another, creating a blended sound within the same syllable. By recognizing and mastering diphthongs, individuals can enhance their pronunciation skills and improve their overall oral communication.
Diphthongs play a significant role in the English language, and understanding their pronunciation is crucial for effective communication.
Categories of Vowel Sounds
Front Vowel
Front vowels are pronounced with the highest part of the tongue pushed forward in the mouth and somewhat arched. Examples of front vowels include:
- The “a” in “had”
- The “e” in “bed”
- The “i” in “fit”
Central Vowel
Central vowels are produced with the tongue in a position closer to the middle of the mouth, neither pushed forward nor raised towards the soft palate. An example of a central vowel is:
- The “ə” in unstressed syllables, such as the “a” in “about”
Back Vowel
Back vowels are pronounced with the back part of the tongue raised towards the soft palate. Examples of back vowels include:
- The “u” in “rule”
- The “o” in “pole”
These categories help us understand the different positions of the tongue and the resulting sounds produced. Mastering the nuances and variations within each category is crucial for clear and precise oral expression.
Short vs. Long Vowels
Short and long vowels are two distinct categories of vowel sounds in the English language. Understanding the difference between these two types of vowels is essential for clear and precise oral expression. Let’s take a closer look at each type and explore some examples.
Short Vowels
Short vowels are vowel sounds that are pronounced briefly and do not have an extended duration like long vowels. In English, there are five primary short vowel sounds:
- /æ/: This sound is commonly represented by the letter “a” (e.g., cat, hat) and occasionally by “ai” (e.g., rain, said).
- /ɛ/: The short “e” sound can be represented by the letter “e” (e.g., bed, red) and “ea” (e.g., head, bread).
- /ɪ/: This sound is usually represented by the letter “i” (e.g., sit, hit) and occasionally by “y” (e.g., gym, symbol).
- /ɒ/: The short “o” sound can be represented by the letter “o” (e.g., dog, hot) and occasionally by “a” (e.g., watch, want).
- /ʌ/: This sound can be represented by a curved symbol above the vowel (e.g., ŭ), but it is usually represented by the letter “u” (e.g., tub, love).
When we say a short vowel sound, the sound is not prolonged, and it is usually represented by a single letter. Mastering these short vowel sounds is crucial as they appear in numerous English words.
Long Vowels
In contrast to short vowels, long vowels are vowel sounds that sound like you are saying the letter itself. Long vowels have an extended duration when pronounced. The five vowels in the English language can make long vowel sounds.
Here are some examples of long vowel sounds:
- /iː/: This sound is typically represented by the letter “e” (e.g., see, tree) and occasionally by “ea” (e.g., tea, sea).
- /eɪ/: The long “a” sound can be represented by the letter “a” (e.g., mate, cake) and occasionally by “ai” (e.g., train, pain) and “ei” (e.g., eight, weight).
Do Vowels Exist in Other Languages?
In the study of linguistics, vowels are a fundamental aspect of speech sounds across various languages. While the specific vowel sounds may differ from language to language, the concept of vowels exists universally. Let’s explore the existence of vowels in other languages and how they compare to the English language.
Vowels in Different Languages
- Spanish: Like English, Spanish has five vowels – A, E, I, O, and U. However, the pronunciation of these vowels may differ slightly, with Spanish vowels typically being more crisp and pure. For example, the Spanish “A” is pronounced as in “father,” while the English “A” has a broader sound.
- French: French is known for its nasal vowels, which are produced with air flowing through the nose. French vowels include A, E, I, O, U, and sometimes Y. The pronunciation of French vowels can be quite distinct and nuanced, with various regional accents adding further variations.
- German: German also has a set of vowels similar to English, consisting of A, E, I, O, U, and sometimes Y. However, German vowels can have slightly different phonetic representations, leading to variations in pronunciation. For example, the German “U” is pronounced closer to the English “OO” as in “good.”
- Japanese: In Japanese, vowels are also considered important sounds. Japanese vowels are A, I, U, E, O, and they are generally pronounced with short and crisp sounds. The vowel length in Japanese is consistent and does not have the same distinction between short and long vowels as in English.
Importance of Recognizing Vowel Differences
Understanding the existence and unique characteristics of vowels in different languages is essential for effective communication and language learning. By recognizing and distinguishing the nuances of vowel sounds, we can improve our pronunciation, comprehension, and fluency in foreign languages.
Furthermore, recognizing vowel differences can also enhance our appreciation for the diversity and richness of languages around the world. Each language has its own set of vowel sounds, contributing to its unique melody and rhythm.
While the specific vowel sounds may vary across languages, the fundamental concept of vowels exists universally. By acknowledging and practicing these differences, we can become more skilled in communicating across languages and cultures.
Conclusion
In this article, I have provided a comprehensive overview of the different types of vowels and their significance in effective communication. We have explored the syllabic nature of vowels and distinguished them from similar sounds lacking this characteristic. Additionally, we have delved into the various categories of vowel sounds in the English language, including short vowels, long vowels, diphthongs, vowels before historical “R,” and weak vowels.
Understanding the nuances and mastering the sounds of vowels is essential for clear and precise oral expression. By exploring the different positions of the tongue and the resulting sounds produced, we can gain a deeper understanding of front vowels, central vowels, and back vowels. Moreover, we have discussed the distinction between short and long vowels, providing examples and explanations for each type.
Furthermore, we have touched upon the existence of vowels in other languages, such as Spanish, French, German, and Japanese. Recognizing the differences in pronunciation and phonetic representations between languages enhances our appreciation for the diversity and richness of languages worldwide.
By familiarizing ourselves with the different types of vowels and their variations, we can improve our pronunciation, comprehension, and fluency in both English and foreign languages. So, let’s continue to explore and master the fascinating world of vowels for effective communication and language learning.



