Embark on another intriguing exploration of human anatomy with our article titled “Body Parts That Start With B.” This fascinating dive into the intricacies of our biological design zeroes in on those parts of our bodies that start with the letter ‘B’. From the vital organ that is the brain to the microscopic components like basal cells, we will uncover the functions, structures, and remarkable details of these parts.
This article is an excellent resource for students, teachers, or anyone with an interest in understanding the marvels of the human body. Whether you’re a budding medical student or an enthusiastic layman, join us as we continue to appreciate the amazing complexity of our bodies, letter by letter.
Human Body Parts That Start With The Letter B
The human body is a marvel of nature, a complex network of systems, structures, and cells that keep us alive and functioning. It is a veritable alphabet of anatomical parts and pieces, many of which begin with the letter ‘B.’ This article explores these ‘B’ components, shedding light on their functions, purposes, and the pivotal roles they play in the human anatomy.
Brain
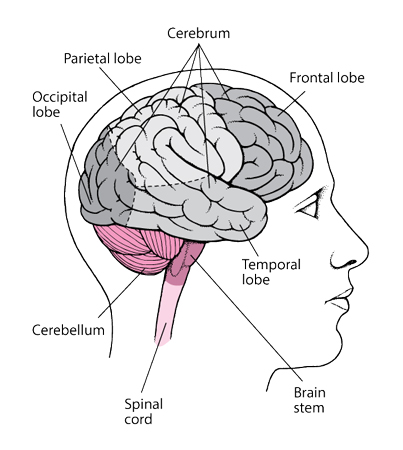
The brain tops the list as one of the most critical organs starting with the letter ‘B’. It’s the control center of the body, nestled within the protective casing of the skull. The brain regulates most bodily functions, from basic needs like breathing and eating to complex processes like thought, memory, feelings, and controlling movement. It is divided into various parts, each with specific responsibilities, such as the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem.
Bladder
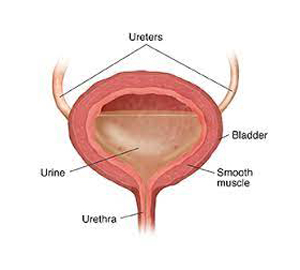
The urinary bladder is a muscular organ that collects and stores urine excreted by the kidneys before disposal by urination. It expands and contracts in response to the volume of urine it holds, which typically ranges from 600 to 800 milliliters. Any issues with bladder control can lead to conditions such as incontinence or urinary tract infections.
Bronchi
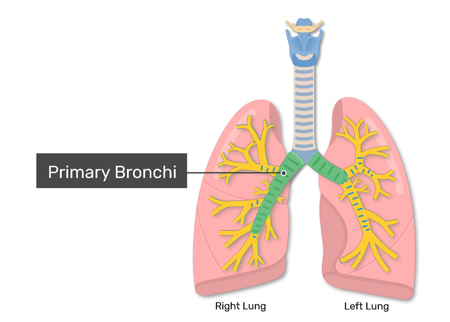
The bronchi are major air passages of the lungs that diverge from the windpipe (trachea). They branch into smaller tubes, which lead to the lobes of the lungs. The primary function of the bronchi, much like the rest of the respiratory system, is to allow the passage of air to and from the lungs for oxygen absorption and carbon dioxide expulsion.
Bones
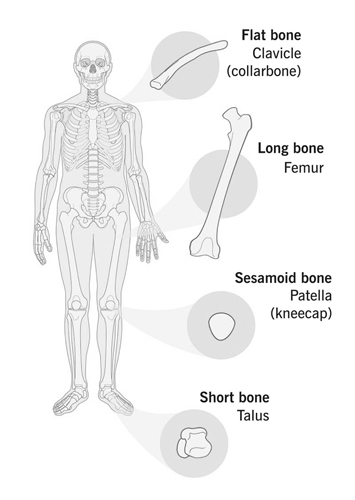
Bones are rigid organs that make up the human skeleton. They serve a myriad of vital functions, including supporting the body, providing structure, protecting organs, facilitating movement (in conjunction with muscles), and producing red and white blood cells. The human body consists of 206 bones, divided into categories such as long bones, short bones, flat bones, and irregular bones.
Biceps
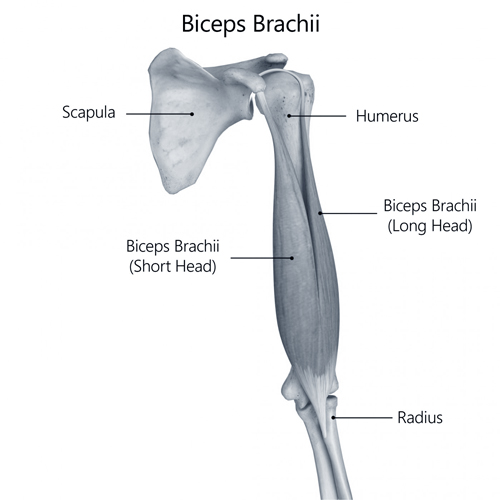
The biceps, officially known as biceps brachii, is a large muscle that lies on the upper arm between the shoulder and the elbow. This muscle is primarily involved in the movement and stabilization of the shoulder and elbow joints. Its main function is to allow rotation of the forearm and flexion of the elbow.
Bile
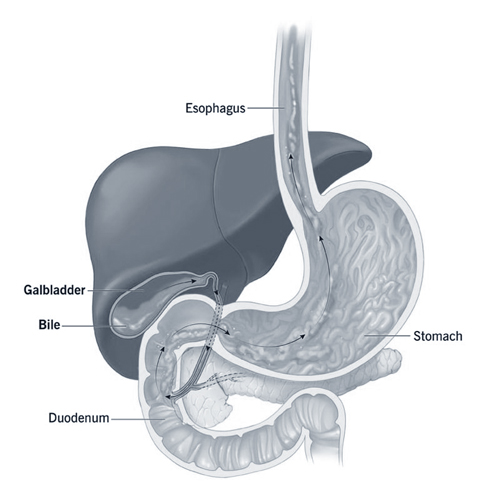
While not a ‘part’ in the conventional sense, bile plays a critical role in the human body. Bile is a bitter, dark green to yellowish brown fluid produced by the liver and stored in the gallbladder. It aids in the digestion of lipids (fats) in the small intestine. Without bile, our bodies wouldn’t be able to process and absorb the fats from our diet effectively.
Blood
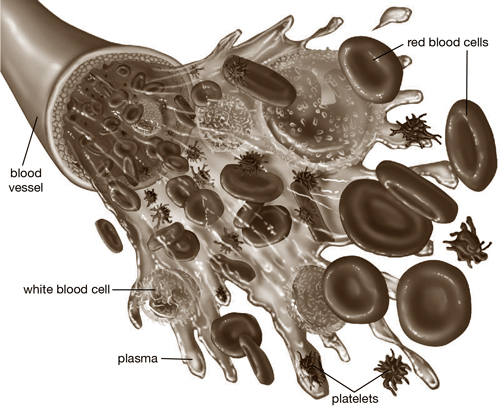
Blood is a specialized bodily fluid that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Composed of red and white blood cells and platelets suspended in a liquid plasma, blood is vital for life. It’s also a key component of the body’s immune response, carrying cells and antibodies that fight infection.
Breasts
Breasts are a pair of mammary glands extending from the front of a woman’s chest. They are responsible for the production of milk in females after childbirth, a process regulated by hormones. The size, shape, and contour of breasts vary significantly among women, and they continue to serve an essential role in both reproductive health and cultural contexts.
Buttocks
The buttocks are two rounded portions of the anatomy, located on the posterior of the pelvic region. Composed largely of muscle and fat, the buttocks help support weight while standing, particularly when leaning back, and they form the exterior contour of the hips. They also serve as a cushion for the sit bones when sitting.
Back Muscles: Your Body’s Powerhouse
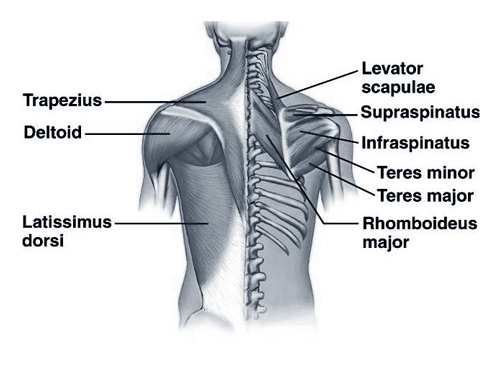
Imagine a superhero’s cape made of countless tiny warriors – that’s your back muscles! These hardworking heroes, numbering over 30 pairs, stretch from your neck to your pelvis, forming a complex network of power and support. They allow you to stand tall, twist, bend, and lift, playing a crucial role in everything from throwing a ball to picking up a backpack.
Here are some amazing facts about your back muscles:
- The strongest: The erector spinae, tucked deep within your spine, are the powerhouses of your back, responsible for straightening and supporting your posture. They can generate enough force to lift several times your body weight!
- The multitaskers: From tiny muscles that move your head to broad sheets that pull your shoulders, your back muscles work together in an intricate dance. They help you breathe, maintain balance, and even swing your arms while walking.
- The team players: Back muscles don’t work alone. They partner with abdominal muscles on the front of your body to create a stable core, essential for all movement.
Remember, keeping your back muscles strong and flexible is key to good posture, preventing injuries, and living a pain-free life. Encourage your kids to exercise regularly, focusing on activities like swimming, yoga, and core-strengthening exercises.
Basilic Vein: The Blue Highway of Your Arm
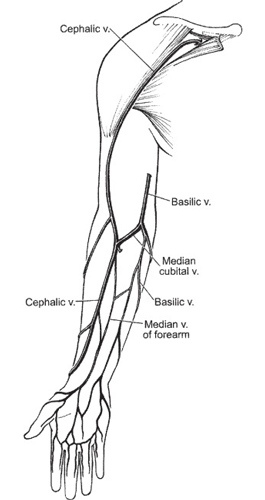
Imagine a winding river snaking from your elbow to your armpit, carrying away the blue tide of deoxygenated blood – that’s the basilic vein! This vital vessel, the longest superficial vein in your arm, plays a crucial role in your circulatory system.
Here are some interesting facts about the basilic vein:
- The location: The basilic vein runs along the inner side of your forearm, easily visible under the skin. Its name comes from the Greek word “basilikos,” meaning “royal,” reflecting its prominent position.
- The workhorse: This vein carries deoxygenated blood from your hand and forearm back to your heart. It plays a vital role in regulating your body temperature by sending excess heat to your skin.
- The accessible: The basilic vein is often used for blood tests and intravenous injections due to its easy accessibility. You may have even seen nurses draw blood from this vein in your arm!
Understanding the basilic vein helps children appreciate the incredible network of veins and arteries that keep us alive and well. Encourage them to learn about their veins and arteries through fun activities like tracing their veins on their arm or building models of the circulatory system.
Biliary Tract: The Silent Chef of Digestion
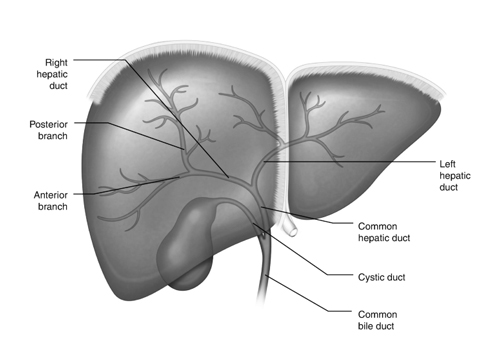
Imagine a hidden system of tiny pipes delivering delicious sauce to your food – that’s your biliary tract! This crucial network of ducts transports bile, a greenish-yellow fluid made by your liver, to your intestine, where it plays a vital role in digestion.
Here are some interesting facts about the biliary tract:
- The team player: Bile helps break down fats in your food, making them easier to digest and absorb. It’s like a tiny chef adding the perfect sauce to your meal!
- The intricate network: The biliary tract consists of a complex system of ducts, including the hepatic ducts, cystic duct, and common bile duct. These ducts join together to deliver bile to your small intestine.
- The silent worker: Unlike your stomach or intestines, the biliary tract works silently and discreetly behind the scenes. Most people are unaware of its important role until something goes wrong, like gallstones forming in the ducts.
Teaching children about the biliary tract helps them understand the complex process of digestion. Encourage them to learn about other digestive organs through fun activities like drawing pictures of the digestive system or building models with playdough.
Bone Marrow: The Factory of Life Inside Your Bones
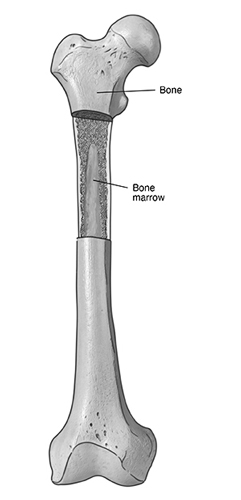
Imagine a bustling factory hidden within your bones, tirelessly producing vital components for your body – that’s your bone marrow! This soft, sponge-like tissue housed within your bones plays a crucial role in blood production, immunity, and bone health.
Here are some amazing facts about the bone marrow:
- The multitasker: Bone marrow doesn’t just make one thing; it’s a true multitasker! It produces three main types of blood cells: red blood cells that carry oxygen, white blood cells that fight infections, and platelets that help your blood clot.
- The power of stem cells: Within the bone marrow lie special cells called stem cells. These “master cells” have the potential to develop into any other cell type in the body, making them crucial for regeneration and repair.
- A lifelong journey: Interestingly, red blood cells only live for about 120 days, while white blood cells have varying lifespans. This means your bone marrow is constantly working to generate new cells throughout your life.
Understanding the importance of bone marrow helps children appreciate the incredible processes happening inside their bodies. Encourage them to learn more about blood production through fun activities like making a model of a bone with red and white blood cell cutouts.
Brachial Plexus: The Conductor of Your Arms
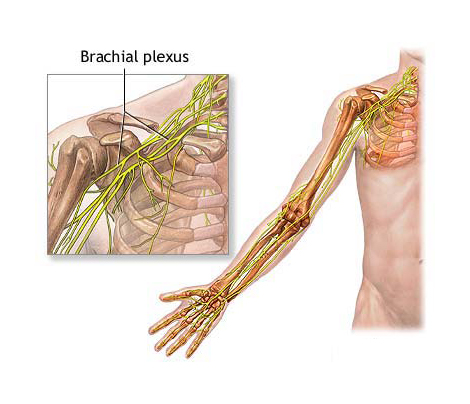
Imagine a complex network of wires connecting your brain to your arms, allowing you to move them with precision – that’s your brachial plexus! This intricate network of nerves is the conductor of your upper limbs, responsible for all your arm and hand movements.
Here are some interesting facts about the brachial plexus:
- The highway of signals: The brachial plexus consists of five pairs of nerves that originate from your spinal cord and branch out to your shoulders, arms, and hands. These nerves carry signals from your brain to your muscles, telling them how to move.
- The master of movement: The brachial plexus controls everything from reaching for a toy to playing the piano. It allows you to bend your elbows, rotate your wrists, and grip objects with your fingers.
- The delicate network: Unfortunately, the brachial plexus is also vulnerable to injury due to its location. Damage to these nerves can affect movement and sensation in your arms and hands.
Teaching children about the brachial plexus helps them understand the importance of taking care of their bodies and avoiding injuries. Encourage them to learn about different nerves and their functions through activities like drawing a simple diagram of the nervous system or playing movement games that involve coordination.
Bronchioles: The Tiny Tubes of Your Lungs
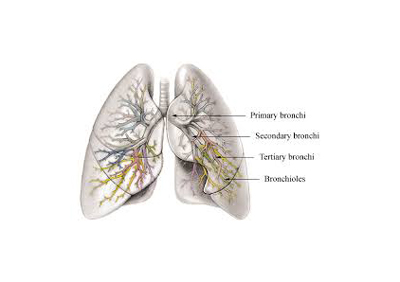
Imagine a tree branching out within your chest, carrying air deep into your lungs – that’s your bronchial system! This network of tubes, including the trachea and bronchi, eventually narrows down to tiny branches called bronchioles. These delicate structures play a crucial role in gas exchange, delivering oxygen to your blood and removing carbon dioxide.
Here are some interesting facts about the bronchioles:
- The air highways: Bronchioles are lined with cilia, tiny hair-like structures that sweep mucus and debris out of your lungs. They also have smooth muscle that can contract and relax, adjusting the airflow within your lungs.
- The team players: Bronchioles work together with alveoli, tiny air sacs where gas exchange happens. Oxygen diffuses from the bronchioles into the alveoli, while carbon dioxide moves in the opposite direction.
- The vulnerable network: Unfortunately, bronchioles are susceptible to irritation and inflammation from pollutants, allergens, and smoking. This can lead to conditions like asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Understanding the bronchioles helps children appreciate the importance of clean air and healthy lungs. Encourage them to learn about the respiratory system through fun activities like building a model of the lungs with balloons or blowing bubbles to visualize air movement.
Basal Ganglia
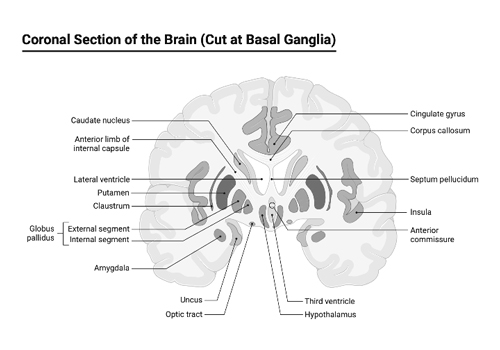
The basal ganglia are a group of subcortical nuclei located at the base of the forebrain, involved in various processes including motor control, behavior, emotions, and learning. Dysfunction of the basal ganglia has been linked to several neurological disorders, including Parkinson’s disease and Huntington’s disease.
Bicuspid Valve
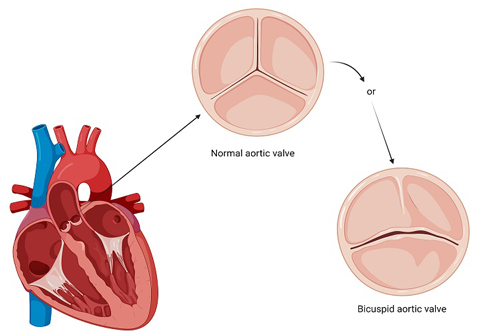
Also known as the mitral valve, the bicuspid valve is one of the four valves in the heart that ensure blood flows in the right direction. It is situated between the left atrium and the left ventricle, allowing blood to flow from the atrium into the ventricle, but not back the other way.
List of Human Body Parts Starting with B
| Back Muscles | Base Of Skull | Basilar Artery |
| Basilic Vein | Bile Duct | Biliary Tract |
| Bladder | Bone Marrow | Bony Labyrinth |
| Brachial Plexus | Brachiocephalic Artery | Brachiocephalic Vein |
| Brain | Bronchi | Bronchioles |
| Bulbo-Spongiosus Muscle | Bones | Biceps |
| Bile | Blood | Breasts |
| Buttocks | Basal Ganglia | Bicuspid Valve |
Conclusion
The human body, in its wisdom, houses numerous parts, systems, and structures that begin with the letter “B.” Each has unique roles and functions that contribute to our survival, making life possible. From the brain, our command center, to the bones that hold us upright, the “B” section of our biological dictionary is filled with vital parts that remind us of the incredible complexity and wonder of the human body.
Human Body Parts That Start With
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W