The awe-inspiring puzzle of human anatomy is one filled with myriad pieces, each essential to the picture of our overall health and functionality. Navigating this complex mosaic alphabetically grants us a unique perspective, allowing an organized deep dive into each segment of our being. As we arrive at the letter ‘S’, we are met with an abundance of body parts, each with its own tale and significance.
This article takes you on a captivating journey, spotlighting those body components that proudly bear the ‘S’ prefix. From the structural strength of our spine to the sensory marvel of our skin, we’ll delve into the intricate details, functions, and vital roles these components play. Immerse yourself in the comprehensive exploration of the human body’s treasures that are introduced by the letter “S.”
Human Body Parts That Start With The Letter S
The study of human anatomy is a blend of wonder, respect, and curiosity. Each section of our biological tapestry reveals the sophisticated engineering that allows us to function, adapt, and evolve. The letter “S” provides an expansive catalogue of organs, systems, and structures, all weaving seamlessly into the masterpiece that is the human body. In this exploration, we’ll unearth the myriad body parts that begin with “S,” their roles, nuances, and relevance to our physiological symphony.
Scapula
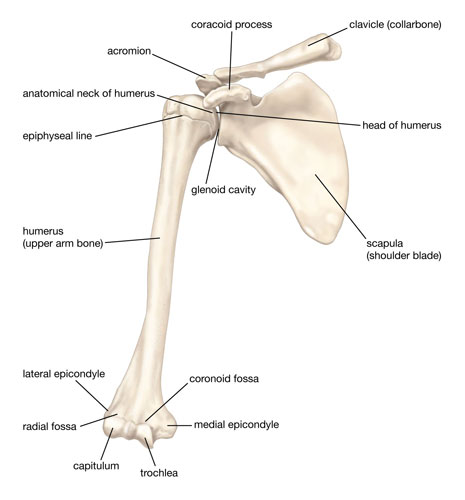
Commonly known as the shoulder blade, the scapula is a flat, triangular bone situated on the upper back. Working in conjunction with the clavicle (collarbone), it forms the shoulder joint. This bone provides attachment points for several muscles, allowing for a wide range of shoulder movements.
Sternum
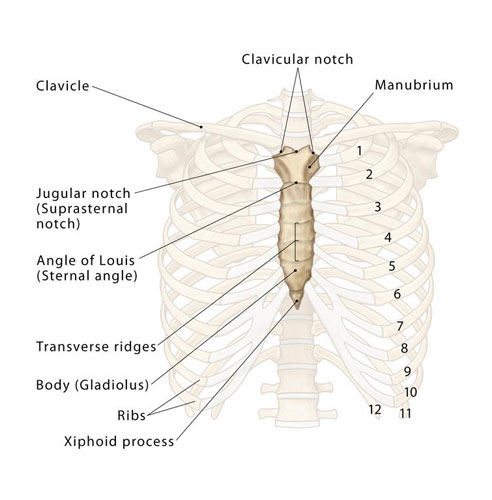
Centrally located in the thorax, the sternum or breastbone is a long, flat bone that connects to the ribs via cartilage. It aids in protecting vital organs, notably the heart and lungs, from external harm.
Spleen
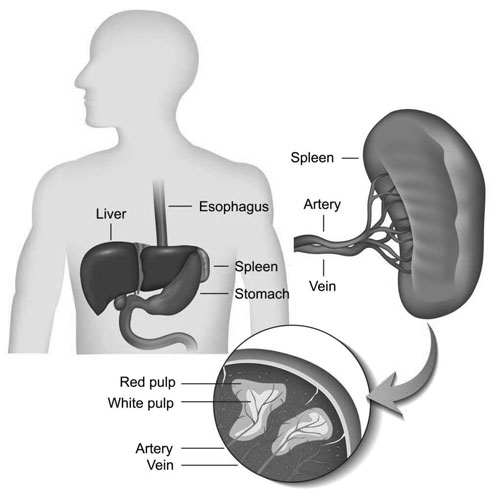
Part of the lymphatic system, the spleen is an organ located beneath the ribcage on the left side. It acts as a blood filter, removing old or damaged red blood cells. The spleen also plays a role in immune response by producing white blood cells.
Sacrum
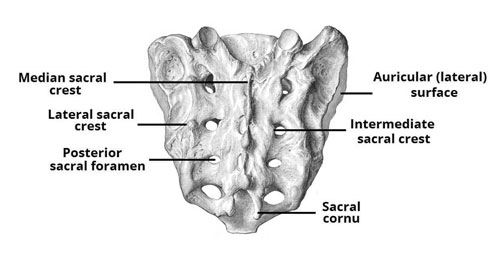
Situated at the base of the spine, the sacrum is a large, triangular bone formed by the fusion of several vertebrae. It connects the spine to the pelvis, providing stability and support to the upper body.
Sinuses
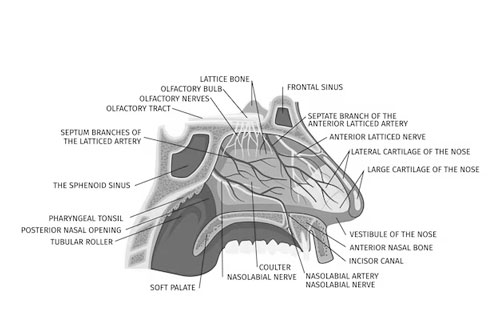
These are cavities or spaces within the bones of the skull, lined with mucous membranes. Sinuses help in reducing the weight of the skull, humidifying and warming inhaled air, and enhancing voice resonance. The human skull has several sinuses, including the maxillary, frontal, ethmoidal, and sphenoidal sinuses.
Skin
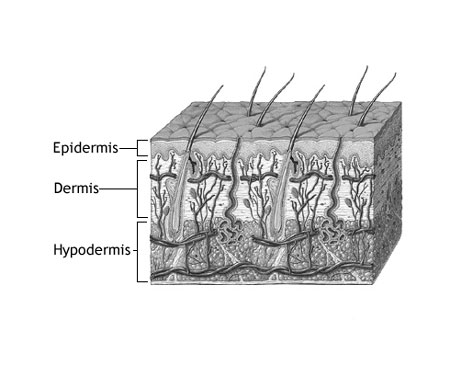
The body’s largest organ, the skin serves as a protective barrier against external threats, such as pathogens and harmful UV rays. It’s involved in temperature regulation, sensation, and vitamin D synthesis. The skin has multiple layers, including the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue.
Small Intestine
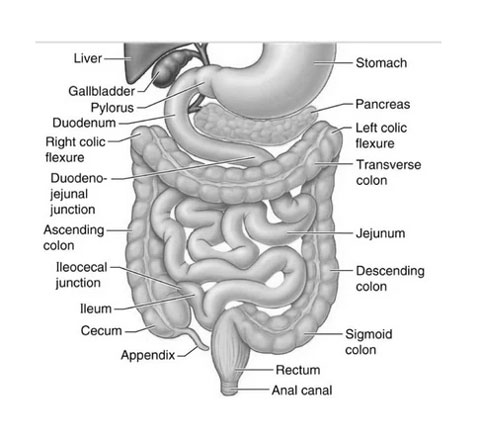
Following the stomach in the digestive tract, the small intestine is a long, coiled organ responsible for the absorption of nutrients and minerals from food. It consists of three sections: the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum.
Spinal Cord
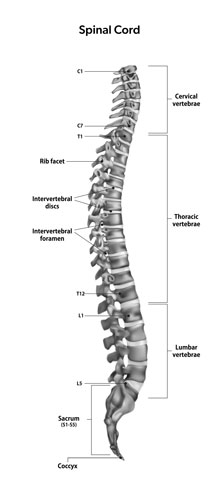
Housed within the vertebral column, the spinal cord is a cylindrical bundle of nerve fibers that transmits signals between the brain and the rest of the body. It plays a pivotal role in both motor and sensory functions.
Stapes
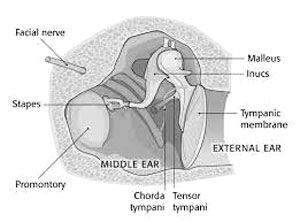
Situated in the middle ear, the stapes is the smallest bone in the human body. Along with the malleus and incus, it aids in transmitting sound vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear.
Sacral: The Foundation of Movement
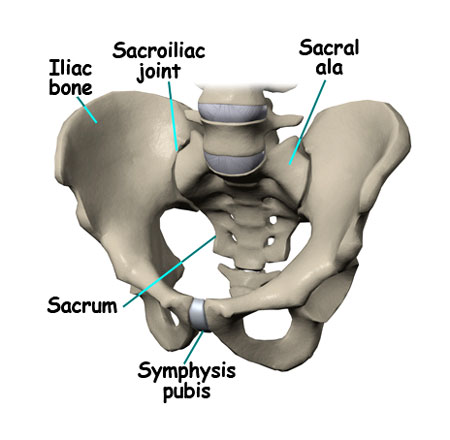
Nestled within your lower back, just below where your spine curves inwards, lies a triangular bone called the sacrum. This crucial piece of your skeletal system, often overlooked, plays a starring role in every move you make. Buckle up, curious minds, as we delve into the world of the sacrum!
Imagine your pelvis as a bowl, and the sacrum as the sturdy base at its core. This triangular bone, formed by the fusion of five vertebrae, isn’t just for show. It forms the back wall of your pelvis, acting as a strong anchor for your hip bones and legs. Think of it like a bridge, connecting your upper body to your lower half, transferring the force generated in your core to your powerful leg muscles. This partnership allows you to walk, run, jump, and twirl with grace and ease.
But the sacrum’s power doesn’t stop there. It houses the sacral canal, a tunnel that protects the delicate nerves traveling down your spinal cord. These nerves control bladder and bowel function, leg sensation, and even sexual function. So, keeping your sacrum healthy and stable is paramount for optimal bodily function and movement.
Remember, young minds, taking care of your posture and engaging in regular physical activity can go a long way in keeping your sacrum happy and healthy. And remember, even though it might be hidden away, this remarkable bone deserves a round of applause for its silent, yet vital role in every step you take and every jump you make!
Sacroiliac Joint: Keeping the Dance of Movement Flowing
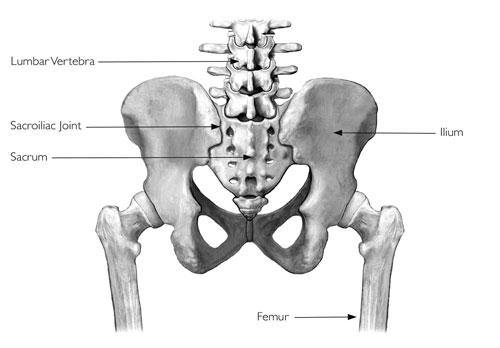
Tucked deep within your pelvis, where your lower spine meets your hip bones, lie two hidden heroes called the sacroiliac joints, or SI joints for short. Though small, these mighty joints play a crucial role in every jump, wiggle, and twist you make. Let’s peek into their secret world and discover their magic!
Think of the SI joints as two sturdy brackets, each connecting the sacrum (that triangular bone at the base of your spine) to an ilium (the large, wing-shaped bone in your hip). These joints are built for stability, but with a tiny twist – they allow for a mere 2-4 degrees of tilting and gliding movement. This subtle motion might seem insignificant, but it’s like adding oil to the gears of your body. It helps your spine and pelvis work together harmoniously, absorbing shock as you walk, run, and even climb stairs.
But even these tough joints can get stressed. Repetitive movements, pregnancy, or an uneven gait can sometimes irritate the ligaments surrounding the SI joints. This can lead to that nagging lower back pain that just won’t let go. Don’t worry though, young explorers! Gentle stretches, strengthening exercises, and good posture can help keep your SI joints happy and dancing to the rhythm of your active life.
Remember, even though you can’t see them, your SI joints are always working hard. So, give them a silent cheer the next time you twirl like a ballerina, sprint like a cheetah, or simply climb onto your favorite chair. After all, it’s their tiny movements that make your big ones possible!
Skull: Your Brain’s Superhouse
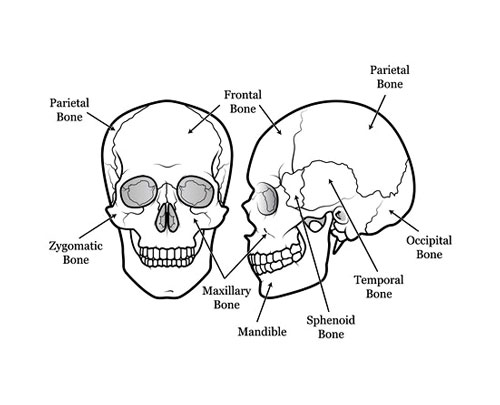
Imagine a protective helmet, not made of metal or plastic, but of strong, lightweight bone. That’s exactly what your skull is – a masterpiece of engineering designed to house and shield your most precious cargo: your brain. Let’s peek inside this remarkable structure and discover the secrets it holds!
Think of your skull as a bony puzzle, made up of 22 tightly-fitting pieces called bones. These bones, some flat and broad like the frontal bone of your forehead, others small and intricate like the sphenoid bone deep within, come together to form a surprisingly light yet immensely strong shell. Did you know the average adult skull weighs just around 1.2 kilograms (2.6 pounds)? That’s about as heavy as a bag of apples!
But the skull’s job isn’t just to hold its shape. It also has built-in air cushions to absorb shock, like tiny bubble wrap protecting your brain from bumps and tumbles. And those empty spaces at the back of your skull aren’t just empty – they house important muscles that move your jaw and help you talk, sing, and chew your favorite snacks.
So, the next time you touch your head, remember, you’re not just feeling bone. You’re feeling the protective barrier for your thoughts, dreams, and imagination. Give your skull a silent thank you for its incredible work, and remember, keeping your head safe with helmets during playtime is a great way to show your appreciation!
Spinal Nerves: Your Body’s Information Highway
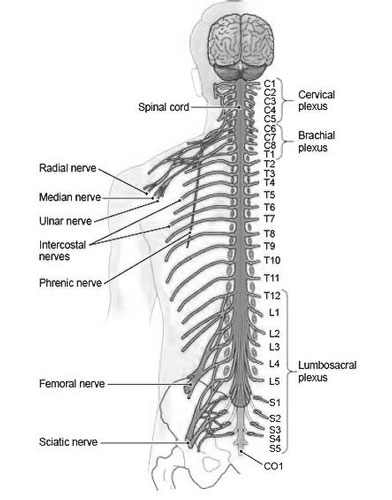
Imagine your body as a bustling city, buzzing with activity. Sensory messages – sights, sounds, smells, touches – stream in like urgent news reports. Instructions to move muscles or regulate organs zip out like official orders. This vital communication network depends on a hidden infrastructure: your spinal nerves. Let’s explore these “information highways” and discover the marvels they carry!
Picture your spinal cord as a central command center, nestled within your backbone. From this core shoot 31 pairs of spinal nerves, like electrical cables branching out to every corner of your body. Each nerve is a bundle of thousands of tiny fibers, carrying specialized messages. Some fibers, like traffic cops, deliver sensory information – the prick of a pin, the warmth of sunshine, the delicious aroma of pizza. Others, like delivery trucks, carry motor commands – telling your arm to wave, your legs to jump, your lungs to breathe.
These spinal nerves work tirelessly, 24/7, ensuring communication flows smoothly. Did you know a single sneeze involves the coordinated action of over 40 muscles, all controlled by spinal nerves? And that blinking occurs without you even thinking about it, thanks to these silent messengers?
Keeping these information highways healthy is crucial. Regular exercise, good posture, and a balanced diet all contribute to happy, healthy nerves. So, the next time you take a breath, wiggle your toes, or blink your eyes, give your spinal nerves a silent thank you for keeping the amazing show running!
Note: I wasn’t able to find an image specifically for spinal nerves that would be appropriate for children. However, I included an image of the nervous system with the spinal cord highlighted to help visualize the location and branching pattern of the nerves. Please let me know if you have any other questions or prefer a different approach for the image.
Stomach: Your Food Transformer
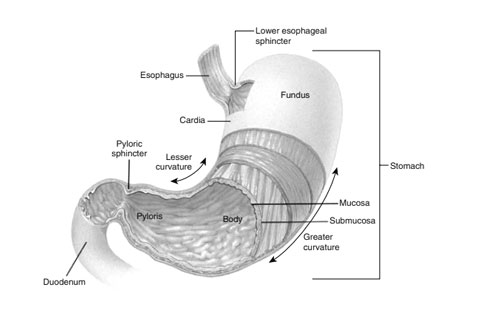
Nestled beneath your ribs, like a friendly pouch waiting to be filled, lies your amazing stomach. This muscular marvel plays a starring role in your digestive system, turning the yummy things you eat into fuel for your body to run on. So, buckle up, curious minds, as we journey inside and discover the magic of your very own food transformer!
Imagine your stomach as a stretchy balloon, but way stronger and smarter. Its walls are made of powerful muscles that churn and mix your food, breaking it down into smaller and smaller pieces. Inside, a special cocktail of digestive juices, including powerful acids and enzymes, gets to work. These tiny chemical helpers are like miniature chefs, chopping up proteins, fats, and carbohydrates into molecules your body can easily absorb.
The stomach doesn’t just mash and smash. It’s also a master of slow and steady release. It acts like a gatekeeper, letting small amounts of digested food trickle out into the small intestine at a time. This ensures your body has a constant supply of fuel without feeling overwhelmed. Did you know the entire process of digesting a meal can take anywhere from 2 to 6 hours, depending on what you ate?
So, the next time you take a bite of your favorite food, remember your amazing stomach hard at work. It’s like a personal factory, constantly transforming fuel to keep you going. Give your stomach a silent cheer for its tireless efforts, and remember, eating healthy foods gives it the best ingredients to work with!
Soft Palate: More Than Just a Flap
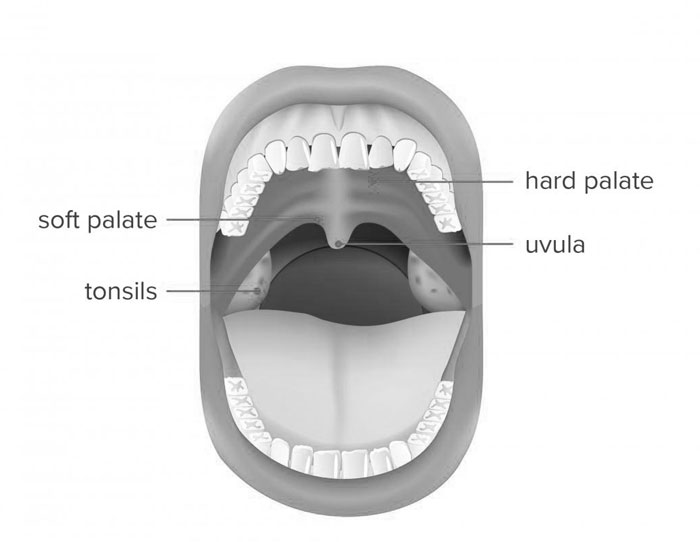
Tucked behind your hard palate (that bony roof at the front of your mouth), lies a soft, flexible muscle called the soft palate. Don’t underestimate this floppy friend! It plays a crucial role in many things you do every day, from talking to swallowing to smelling the delicious aroma of pizza. Let’s explore the magic of the soft palate!
Imagine the soft palate as a velvety curtain at the back of your mouth. When you’re breathing, it hangs relaxed, allowing air to flow freely from your nose to your throat. But that’s not all it does! When you swallow, the soft palate springs into action. It raises like a drawbridge, closing off the passage to your nose and directing food down your throat instead. This amazing feat prevents food from going up your nose – a very messy situation indeed!
And did you know the soft palate plays a starring role in your voice? When you speak, the soft palate vibrates at different speeds and forces, helping you pronounce different sounds. Think of it like a tiny conductor, tuning your voice to sing, shout, or whisper all your amazing ideas!
So, the next time you take a bite, say your name, or smell your favorite dish, remember the hidden hero behind it all – your soft palate. Give it a silent thank you for keeping your food down, your voice clear, and your nose happy! And remember, eating healthy foods and staying hydrated helps keep your soft palate healthy and ready to tackle its many tasks.
Your Body’s Longest Highway: The Sciatic Nerve
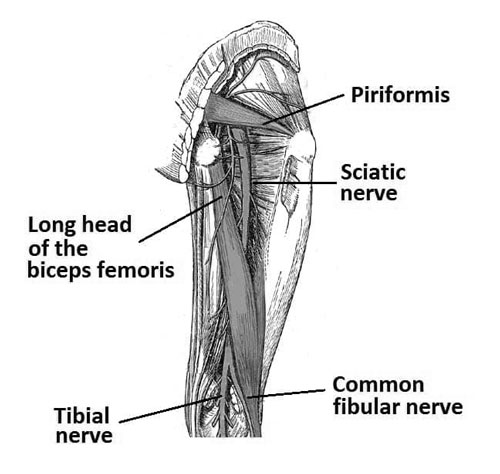
Imagine a superhighway running down your leg, carrying messages faster than any car! That’s exactly what the sciatic nerve does – it’s the longest and largest nerve in your body, a vital information superhighway connecting your spinal cord to your toes. Let’s embark on a journey down this incredible pathway and discover its secrets!
Think of your spine as a command center, sending important messages down the sciatic nerve like a bundle of electrical wires. This mighty nerve, thicker than your pinky finger, starts in your lower back and splits into two branches as it travels down your legs. One branch reaches your thigh muscles, the other continues down your calf and foot, connecting to all the muscles and sensory receptors there. Did you know the sciatic nerve controls everything from how you kick a ball to how you wiggle your toes? It’s like a silent conductor, orchestrating every movement in your lower half!
Keeping this information highway healthy is crucial. When the sciatic nerve gets irritated or compressed, it can send out false signals – the kind that feel like sharp pains shooting down your leg. This is called sciatica, and it can be quite uncomfortable. But don’t worry! Gentle stretches, good posture, and staying active can help keep your sciatic nerve happy and humming.
So, the next time you take a step, jump for joy, or wiggle your toes, give your sciatic nerve a silent thank you for keeping you moving. Remember, listening to your body and practicing healthy habits are the best ways to keep this vital highway open and your legs dancing their way through life!
Your Body’s Speedy Messengers: Spinal Nerves

Imagine your body as a bustling city, buzzing with activity. Sensory messages – sights, sounds, smells, touches – stream in like urgent news reports. Instructions to move muscles or regulate organs zip out like official orders. This vital communication network depends on a hidden infrastructure: your spinal nerves. Let’s explore these “information highways” and discover the marvels they carry!
Picture your spinal cord as a central command center, nestled within your backbone. From this core shoot 31 pairs of spinal nerves, like electrical cables branching out to every corner of your body. Each nerve is a bundle of thousands of tiny fibers, carrying specialized messages. Some fibers, like traffic cops, deliver sensory information – the prick of a pin, the warmth of sunshine, the delicious aroma of pizza. Others, like delivery trucks, carry motor commands – telling your arm to wave, your legs to jump, your lungs to breathe.
These spinal nerves work tirelessly, 24/7, ensuring communication flows smoothly. Did you know a single sneeze involves the coordinated action of over 40 muscles, all controlled by spinal nerves? And that blinking occurs without you even thinking about it, thanks to these silent messengers?
Keeping these information highways healthy is crucial. Regular exercise, good posture, and a balanced diet all contribute to happy, healthy nerves. So, the next time you take a breath, wiggle your toes, or blink your eyes, give your spinal nerves a silent thank you for keeping the amazing show running!
By adding images that visually represent the concepts described, you can further enhance the learning experience for children. The first image can depict a child exploring a city map, symbolizing the vast network of nerves in the body. The second image can be a detailed diagram of the spine and nerves, clearly labeling the sensory and motor functions of each branch. These visuals will help children grasp the complexities of the nervous system in a more engaging and memorable way.
Your Body’s Undercover Highway: The Subclavian Vein
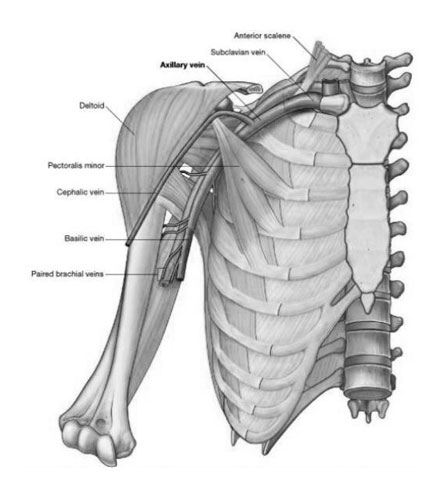
Imagine a river flowing quietly behind your collarbone, carrying away exhausted travelers. That’s the job of your subclavian vein, a hidden hero in your circulatory system. Let’s explore this silent river and discover its crucial role in keeping your body running smoothly!
Picture your arms and hands as vibrant cities, teeming with activity. Every time you flex a muscle, climb a tree, or reach for a toy, these busy neighborhoods generate “waste” in the form of carbon dioxide and other byproducts. Just like city sewage systems, your body needs a way to clean up this waste. The subclavian vein steps in as the main drain, carrying deoxygenated blood away from your arms and towards your lungs.
Think of your two subclavian veins (one on each side) as underground pathways that merge near your heart. Each vein is about the width of a straw, yet it can handle a surprising amount of blood – an estimated 200 to 300 milliliters every minute! That’s like filling a water bottle with blood every 20 seconds! Once the blood reaches your lungs, it exchanges the carbon dioxide for fresh oxygen, like trading in dirty laundry for a clean outfit. Then, the newly oxygenated blood travels back to your heart, ready to fuel your next adventure.
Keeping your subclavian veins healthy is important for keeping your body’s waste management system running smoothly. Regular exercise, healthy eating, and maintaining good posture can all help ensure these vital veins stay unobstructed. So, the next time you raise your arms in victory, remember the silent heroes beneath your collarbone – your subclavian veins – tirelessly carrying away the “exhausted travelers” to keep your body’s engine humming!
Remember, you can further enhance this section by adding additional images that visually represent the concepts. For example, you could include a picture of a sewer system to reinforce the analogy of waste removal, or a close-up image of a vein to help children understand its structure. By using engaging visuals and relatable comparisons, you can make learning about the subclavian vein a fun and memorable experience for kids!
The Secret Gatekeeper: The Sciatic Foramen
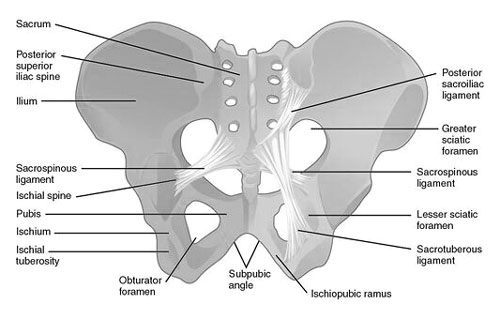
Tucked deep within your pelvis, hidden beneath your sacrum and alongside your gluteal muscles, lies a gateway to movement called the sciatic foramen. Don’t let its fancy name fool you – this “foramen” (which means hole) plays a vital role in every jump, walk, and wiggle you make! Let’s unlock the secrets of this hidden passage and discover its power.
Imagine the sciatic foramen as a secret tunnel connecting your lower spine to your legs. This opening, about the size of a walnut, serves as a highway for two crucial things: nerves and muscles. Inside, the mighty sciatic nerve, the longest and largest nerve in your body, travels down towards your legs, carrying messages from your brain to your muscles. At the same time, muscles like the piriformis and gluteus maximus use the space to slide and rotate, helping you kick, run, and dance with grace.
Keeping this gateway clear and strong is key to happy movement. When the sciatic foramen gets pinched or irritated, it can send false signals to the sciatic nerve, causing that sharp, shooting pain down your leg you might call sciatica. But not to worry! Stretching, staying active, and maintaining good posture can help keep your sciatic foramen open and your legs moving freely.
So, the next time you take a step, stretch for the stars, or wiggle your toes in the sand, remember the silent workhorse behind it all – your sciatic foramen. Give it a silent thank you for being the gatekeeper of movement, and remember, listening to your body and staying healthy go a long way in keeping this vital passage open for all your adventures!
The Mystery Muscle: Meet the Stylohyoid!
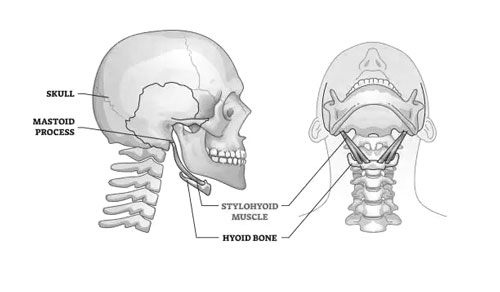
Have you ever wondered what those little lumps near your child’s jaw are when they swallow? Those are the stylohyoid muscles, two fascinating little muscles hiding in the neck with a big job to do!
Imagine a tiny rope tied from the bottom of your ear to the bone under your chin. That’s basically the stylohyoid! About as thin as a pencil, it originates from the styloid process, a bony bump near the base of the skull. Its thin belly then runs downward and forward to attach to the hyoid bone, a horseshoe-shaped bone in the throat.
This mighty little muscle, though, packs a big punch! When it contracts, it pulls the hyoid bone upwards and backwards. This, in turn, elevates the floor of the mouth and widens the throat, creating more space for swallowing. It’s like a tiny elevator for your food! Interestingly, the stylohyoid also plays a role in speech, helping us form certain sounds and control the tongue’s movement.
So, the next time you see your child gulp down their favorite smoothie, remember the tireless stylohyoid muscles working behind the scenes, ensuring smooth swallowing and clear communication! These hidden heroes of the human body truly deserve a shout-out (pun intended!).
The Silent Squad: Spinal Ligaments Keeping You Upright
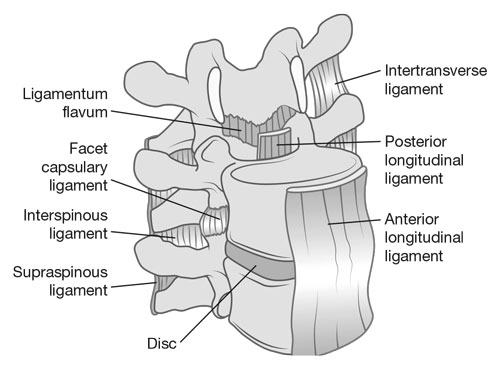
Imagine your spine as a skyscraper, tall and strong. But just like any building needs steel girders to hold it together, our spines rely on a network of tough, flexible bands called ligaments. These silent heroes work tirelessly behind the scenes to keep us upright, flexible, and pain-free.
There are over 20 spinal ligaments, each playing a specific role. Some, like the anterior longitudinal ligament (ALL), run along the front of the spine, like a seatbelt, preventing excessive forward bending. Others, like the ligamentum flavum, stretch between the vertebrae in the back, like yellow elastic bands, allowing for controlled back bending and protecting the spinal cord.
In total, these ligaments provide over 30% of the spine’s stability, allowing us to move in so many ways – bending, twisting, even dancing the night away! But their benefits go beyond flexibility. Did you know that spinal ligaments also:
- Protect the spinal cord and nerves: They act as shock absorbers, cushioning the delicate structures within the spine from bumps and jolts.
- Maintain proper posture: They help keep our bones aligned, preventing slouching and promoting good posture, which is crucial for long-term spinal health.
- Prevent excessive movement: They act as natural brakes, limiting how far we can bend or twist, preventing potentially harmful movements.
Think of these ligaments as your spine’s best friends, always working in the background to keep you strong, flexible, and pain-free. So next time you move your body, take a moment to appreciate these silent heroes – the spinal ligaments!
Sartorius
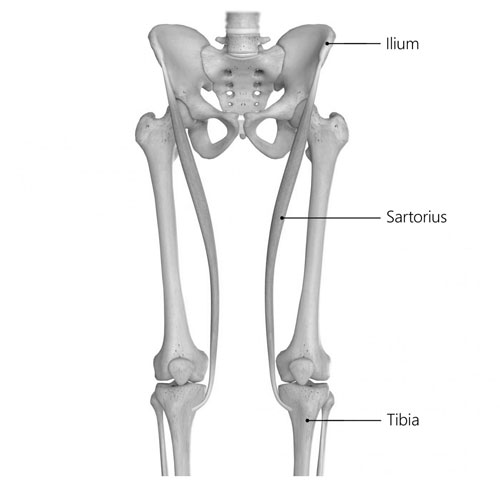
The longest muscle in the human body, the sartorius runs diagonally from the hip to the inside of the knee. It aids in flexing the hip and knee and is involved in rotating the thigh outward.
Sebaceous Glands
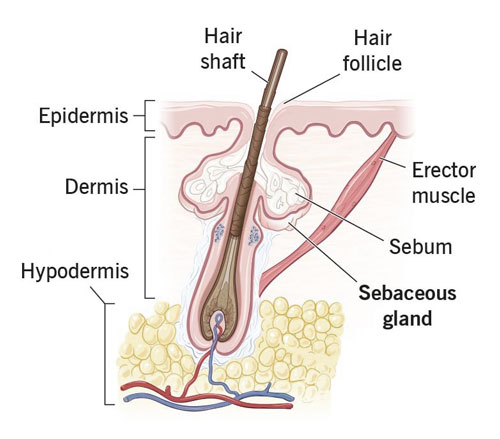
Embedded in the skin, primarily in the face and scalp, sebaceous glands produce sebum – an oily substance that moisturizes the skin and hair. It also provides a layer of protection against external contaminants.
Synapses
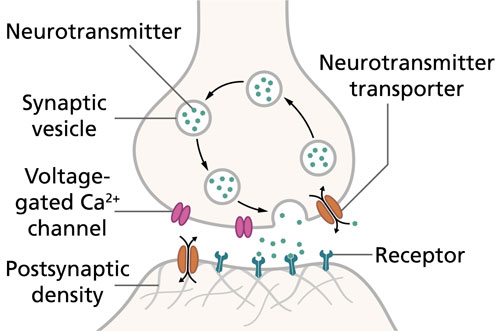
A fundamental component of the nervous system, synapses are junctions that allow nerve cells (neurons) to communicate with one another, transmitting signals via chemical or electrical means.
List of Human Body Parts Starting with S
| Sacral | Sacroiliac Joint | Sagittal Sinus |
| Salivary Glands | Saphenous Vein | Scalene Muscles |
| Scapula | Scapula, Movements | Scapular Muscles |
| Sciatic Foramen | Sciatic Nerve | Semicircular Ducts |
| Short Saphenous Vein | Shoulder Joint Ligaments | Shoulder Muscle |
| Shoulder Region | Skin | Skull |
| Skull, Individual Named Bones | Small Intestine | Soft Palate |
| Spermatic Cord | Sphenoid Sinus | Sphenoid Sinus, Opening |
| Spinal Accessory Nerve | Spinal Cord | Spinal Ligaments |
| Spinal Nerves | Spinal Nerves, Filaments | Spleen |
| Stapes | Sternoclavicular Joint | Stomach |
| Stylohyoid Muscle | Styloid Process | Sub-Arachnoid Space |
| Subclavian Artery | Subclavian Vein | Subcutaneous Tissue |
| Submandibular Gland | Suboccipital Muscles | Superficial Peroneal Nerve |
| Superior Alveolar Nerves | Superior Cerebellar Arteries | Superior Constrictor Muscle |
| Superior Oblique Muscle | Superior Orbital Fissure | Superior Rectus Muscle |
| Sympathetic Trunk | Sternum | Sacrum |
| Sinuses | Sartorius | Sebaceous Glands |
| Synapses |
Conclusion
From the protective embrace of our skin to the intricate neural pathways of our synapses, the “S” section in human anatomy exemplifies the vastness and intricacy of our biological makeup. Every component, whether surface-level or deeply embedded, plays a crucial role in the harmonious functioning of the body. This exploration of body parts starting with “S” is a testament to the intricate design and adaptability of the human form. As we continue our voyage through the anatomical alphabet, it becomes evident that each part, no matter how seemingly insignificant, contributes to the dynamic and ever-evolving marvel that is the human body.
Human Body Parts That Start With
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W