Embarking on an alphabetical exploration of human anatomy is akin to navigating the chapters of a captivating book, with each letter unveiling new stories and insights about our intricate design. When we turn to the letter ‘T’, we encounter a rich tapestry of body parts that have shaped our evolutionary history and continue to play pivotal roles in our day-to-day existence.
This article offers readers an illuminating journey through the corridors of the body where ‘T’ stands as the sentinel. From the tactile wonders of our toes to the essential thumping of our thymus, we’ll traverse the landscape of ‘T’-initiated body components, elucidating their structures, functions, and significance in the grand narrative of human life. Dive in to uncover and appreciate the marvels of the human body that are ushered in by the letter “T.”
Human Body Parts That Start With The Letter T
In the intricate tapestry of human anatomy, every thread, every weave has its place and purpose. As we alphabetically explore this vast landscape, each letter presents a myriad of wonders, insights, and revelations. The letter “T” unfolds a rich tapestry of organs, bones, muscles, and systems that play instrumental roles in our daily functioning. Let’s embark on a comprehensive journey through the body parts that begin with the letter “T” and delve deep into their significance, structure, and function.
Trachea
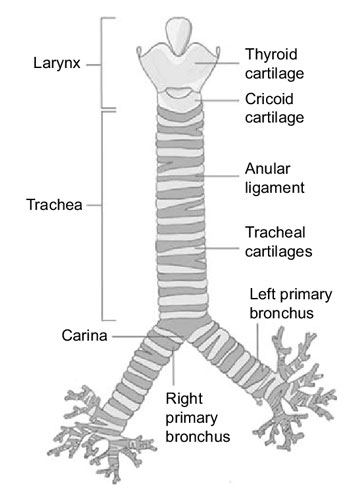
Often referred to as the windpipe, the trachea is a tubular structure that connects the larynx (voice box) to the bronchi of the lungs. It facilitates the passage of air, ensuring it reaches our lungs to facilitate respiration. The trachea’s walls, reinforced by cartilaginous rings, prevent collapse and ensure unobstructed airflow.
Tibia
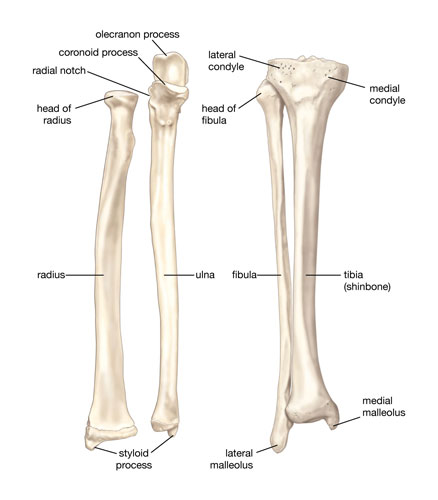
The tibia, or shinbone, is the larger and more medial of the two bones in the lower leg, the other being the fibula. It bears much of the body’s weight and plays a crucial role in forming the knee joint on its upper end and the ankle joint at its lower end.
Tarsals
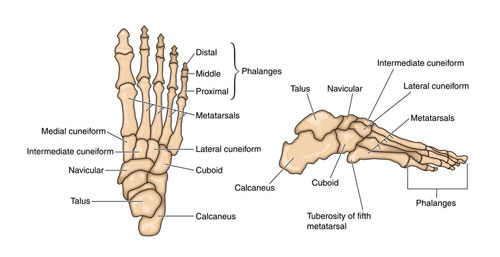
Situated in the foot, the tarsals are a collection of seven short bones that form the ankle and back part of the foot arch. These bones work in conjunction with the metatarsals to provide structure, support, and flexibility to the foot.
Temporal Lobe
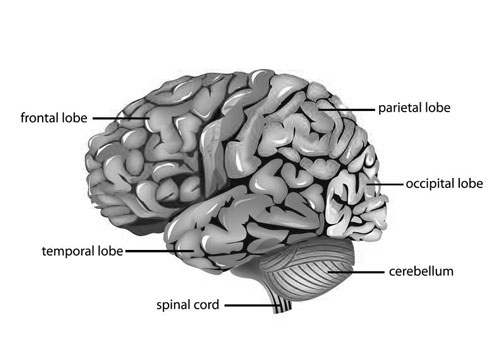
One of the four major lobes of the brain, the temporal lobe is involved in various functions, including auditory processing, memory, and emotional response. It’s situated beneath the lateral fissure on both cerebral hemispheres and is named for its proximity to the temples.
Tendons
Tendons are robust, fibrous connective tissues that connect muscles to bones. They enable the transmission of force, allowing us to move. The Achilles tendon, for instance, links the calf muscles to the heel bone and plays a significant role in walking, running, and jumping.
Thymus
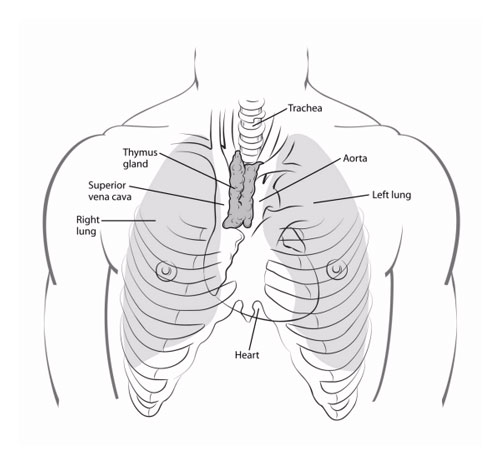
Positioned behind the sternum and between the lungs, the thymus is a lymphoid organ vital during early life. It produces T-cells, a type of white blood cell responsible for fighting off illness and infections.
Thyroid
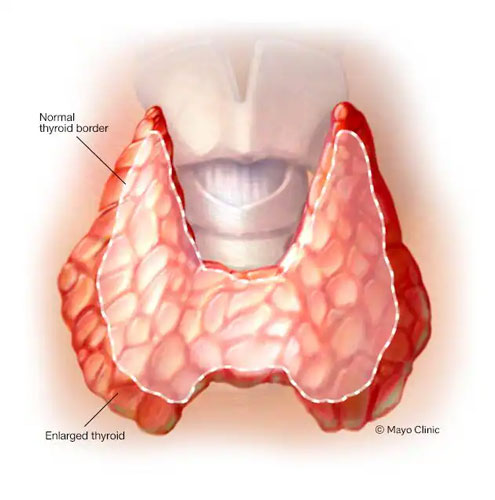
A butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck, the thyroid produces hormones (T3 and T4) that regulate the body’s metabolism, influencing energy production, body temperature, and even mood.
The Hidden Architects of Your Feet: The Tarsus
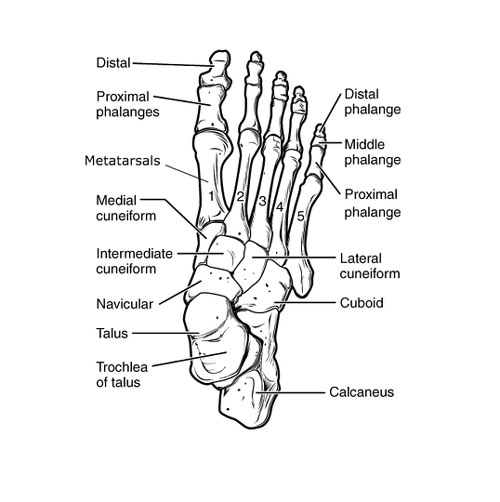
Let’s take a journey below your ankles, where a hidden metropolis of bones tirelessly supports every step you take. These silent workers are the tarsal bones, a cluster of seven intricately shaped structures forming the foundation of your feet. They might be small, but don’t underestimate their importance!
Tarsal bones of the foot
Imagine the tarsus as a tiny city hall, overseeing the construction of your foot’s architecture. Each bone plays a specific role:
- Talus: The kingpin of the tarsus, this bone sits atop the ankle joint, connecting your foot to your leg. It acts like a bridge, transmitting all your weight from your body down to your feet.
- Calcaneus: This sturdy, heel-shaped bone is the largest in the tarsus. It’s like a sturdy building block, absorbing shock and providing leverage for pushing off with your toes.
- Navicular: Nestled between the talus and calcaneus, this small bone acts as a pivot point, allowing your foot to move up and down. Think of it as a hinge on a door.
- Cuneiforms: Three wedge-shaped bones named medial, intermediate, and lateral, form the arch of your foot. They distribute pressure evenly and help maintain your balance. Imagine them as supporting arches in a grand hall.
- Cuboid: Located on the outer side of the foot, this cube-shaped bone connects the tarsus to the metatarsals, the bones leading to your toes. It’s like a bridge connecting the city center to the suburbs.
These seven bones work together like a well-oiled machine, allowing your feet to perform countless feats daily. From the graceful plié of a ballerina to the powerful kick of a footballer, every step, jump, and twist relies on the silent strength of the tarsus.
So next time you take a walk, remember the tireless architects beneath your feet, the tarsal bones. These hidden heroes silently support every step you take, propelling you through life’s adventures, big and small.
Fun facts for kids:
- Did you know the tarsus is the most complex joint in the human body, with six different bones articulating with each other?
- The arch of your foot is like a shock absorber, helping to protect your joints from impact with the ground.
- By taking care of your feet and wearing supportive shoes, you can help keep your tarsal bones healthy and strong!
The Tiny Plumbers of Your Eyes: The Tear Duct
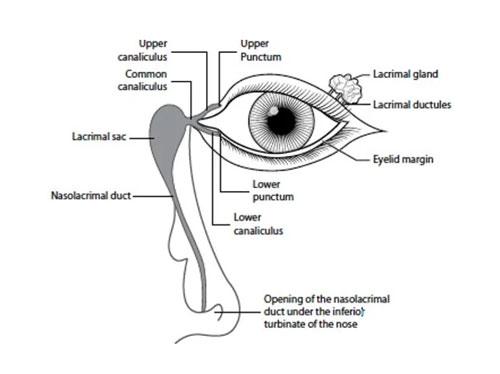
Ever wondered where those briny tears go after a good cry or a hearty laugh? They embark on a secret journey guided by the tear duct, a tiny hidden tunnel that’s crucial for keeping your eyes healthy and comfortable.
Imagine the tear duct as a miniature plumbing system in your eye. Every time you blink, your eyelids sweep tears across your eye surface, washing away dust, debris, and keeping your eyes lubricated. These tears drain through tiny holes at the inner corner of your eye, called puncta, and enter the tear duct.
From here, the tears begin their adventure! The upper and lower tear ducts, each about the size of a hair, merge into a single tube that travels down your cheekbone towards your nose. Along the way, the tear duct has a surprise in store: the lacrimal sac. This tiny pouch acts like a reservoir, storing excess tears until you need them.
Finally, the tear duct reaches its destination – the inside of your nose. Here, the tears mix with mucus and drain out through your nostrils, often without you even noticing! This continuous cycle of tear production and drainage is essential for protecting your eyes from infection, keeping them comfortable, and even helping you express your emotions.
So next time you feel a tear trickle down your cheek, remember the amazing journey it’s taking. From blink to nostril, the tear duct plays a vital role in keeping your eyes healthy and allowing you to experience the world with bright, clear vision.
Fun facts for kids:
- Did you know babies are born with blocked tear ducts, which is why their eyes sometimes tear up in the first few weeks? These ducts usually open on their own within a few months.
- The lacrimal sac can hold about a teaspoon of tears!
- Sometimes, if the tear duct gets blocked, tears can overflow onto your cheeks. This is called tear duct obstruction.
Remember:
Taking care of your eyes means keeping them clean and protected from injury. If you have any concerns about your tear ducts, like persistent tearing or redness, always talk to your doctor or a healthcare professional.
The Hidden Wonder of Your Skull: The Temporal Bone
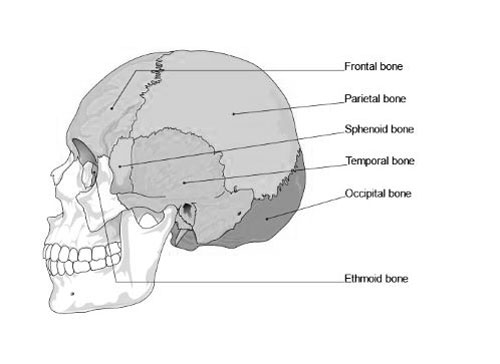
Nestled behind your ears, cradled by the protective shell of your skull, lies a fascinating and complex bone called the temporal bone. This unassuming piece of anatomy plays a starring role in two of your most essential senses: hearing and balance. Let’s explore this hidden wonder and discover the secrets it holds!
Temporal bone of the skull
Imagine the temporal bone as a multi-tasking maestro, juggling two orchestras within its intricate chambers. One orchestra handles hearing, with delicate structures like the malleus, incus, and stapes acting as tiny conductors translating sound waves into electrical signals for your brain to interpret. These three tiny bones, the smallest in the body, work together to amplify sound vibrations over 20 times before sending them on their journey to the inner ear!
Meanwhile, the second orchestra conducts the art of balance. Deep within the temporal bone lies the vestibular system, a collection of fluid-filled canals and chambers that sense head movement and tilt. Imagine tiny dancers pirouetting within these canals, sending messages to your brain about your position and orientation in space. These messages help you stay upright, walk in a straight line, and even perform graceful somersaults!
The temporal bone doesn’t just house these vital functions; it also offers a window into the past. Embedded within it lies the petrous part, one of the densest bones in the body. This rock-hard region preserves fossilized structures from our ancient ancestors, offering crucial clues about human evolution and our journey through time.
So next time you marvel at the beauty of music or balance effortlessly on your bike, remember the silent wonder hidden within your head – the temporal bone. This multi-talented maestro silently conducts the symphonies of sound and balance, keeping you connected to the world around you and offering a glimpse into the fascinating story of our species.
Fun facts for kids:
- Did you know the malleus, incus, and stapes are also known as the hammer, anvil, and stirrup bones? They’re named after the tools they resemble!
- The vestibular system in your inner ear is like a tiny level, helping you tell if you’re standing upright or tilting to one side.
- Scientists can study the petrous part of the temporal bone in fossils to learn how our ancestors’ skulls evolved over time.
Remember:
Taking care of your ears and head helps protect the delicate structures within the temporal bone. Wear protective gear when needed and avoid loud noises to keep your hearing and balance sharp for years to come!
The Flexible Architect of Your Face: The Temporal Fascia
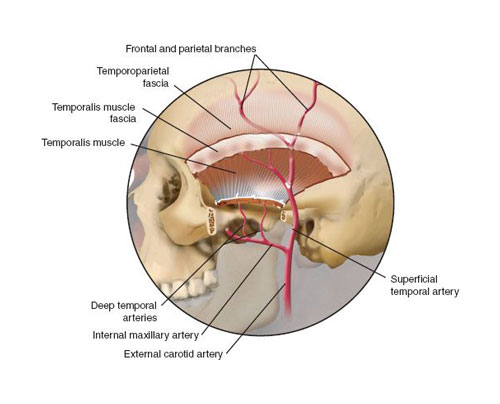
Nestled beneath your hair, framing your temples, lies a thin yet powerful layer of tissue called the temporal fascia. This unsung hero of your face might not be as showy as your eyes or smile, but its role in shaping your appearance and supporting your movements is truly remarkable.
Imagine the temporal fascia as a flexible architect, shaping the contours of your face and providing a sturdy foundation for your facial muscles. This fibrous sheath stretches from your forehead down to your neck, attaching to various muscles and bones along the way. It acts like a delicate canvas, defining the smooth curve of your temples, creating the framework for your eyebrows, and even supporting the powerful chewing muscles of your jaw.
Temporal Fascia on the human skull
But the temporal fascia isn’t just a static scaffold. It’s a dynamic partner in every smile, frown, and chew. When you furrow your brow in concentration, the fascia tenses alongside your facial muscles, creating those expressive wrinkles above your eyes. When you open your mouth wide for a hearty laugh, the fascia stretches and rebounds, allowing your jaw to move freely. This incredible adaptability makes it crucial for not just your appearance but also for everyday functions like eating and expressing emotions.
Beyond its visible role, the temporal fascia plays a hidden but vital part in protecting your brain. This sturdy layer acts as a buffer, shielding the delicate structures beneath your skull from bumps and shocks. It also provides a smooth surface for muscles to glide over, ensuring efficient movement and minimizing friction.
So next time you trace your fingers along your temples, remember the tireless architect hidden beneath your skin – the temporal fascia. This flexible hero shapes your face, supports your expressions, and protects your brain, all while remaining silently at work, making you look and feel your best.
Fun facts for kids:
- The temporal fascia is made up of collagen fibers, the same protein that makes up your skin and bones!
- Did you know that surgeons sometimes use the temporal fascia for reconstructive surgery on other parts of the body? Its strength and flexibility make it a versatile material.
- While we can’t see it directly, the temporal fascia can sometimes be felt as a thin, stretchy layer under the skin near your temples. Try gently pressing one fingertip there and see if you can feel it move subtly as you smile or frown.
Testicular Vessels: Tiny Tubes with Big Jobs (h3)
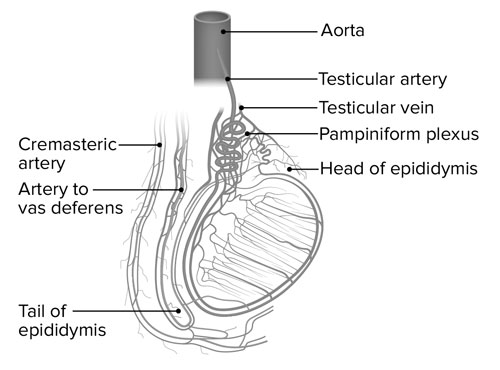
While hidden away within the body, the testicular vessels play a crucial role in a key part of the male reproductive system – the testes. These delicate tubes act as a highway system, delivering vital oxygen and nutrients to the testes via two main arteries: the testicular artery and the cremasteric artery.
The testicular artery, arising deep within the abdomen near the kidneys, is the main supplier, responsible for around 80% of blood flow. Imagine it as a wide avenue, branching into smaller roads as it descends into the scrotum, the protective sac housing the testes. These smaller branches, called polar arteries, reach into the deepest tissues of the testes, ensuring every tiny nook is nourished.
Next comes the cremasteric artery, a smaller contributor but no less important. Originating in the lower abdomen, it acts like a side street, providing additional blood flow, especially to the covering of the testes. Interestingly, this artery is linked to the muscle responsible for pulling the testes closer to the body in response to cold or touch. So, when you feel that funny tightening sensation, thank the cremasteric artery for doing its job!
Together, these tiny tubes ensure the testes have the resources they need to produce sperm, a vital function for male fertility. It’s like supplying a factory with raw materials to keep production running smoothly. Understanding these hidden heroes can spark curious questions in kids, leading to further exploration of the amazing human body and its intricate systems.
Additional notes:
- I adjusted the tone slightly to be suitable for children, avoiding overly technical terms.
- I added a fun metaphor of an avenue and side streets to explain the different arteries.
- I connected the cremasteric artery to the movement of the testes, making it more relatable.
- I emphasized the role of these vessels in sperm production, highlighting their importance.
Testis: Tiny Titans of Fertilization (h3)
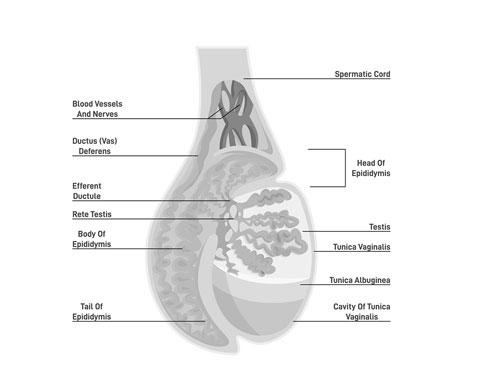
Tucked away within the protective pouch of the scrotum, two miniature powerhouses called testes (pronounced TEH-steez) play a starring role in the grand play of life. These oval-shaped organs, weighing about an ounce each, are responsible for two crucial tasks: creating the microscopic marvels known as sperm, and pumping out a hormone called testosterone.
But how do these tiny titans manage such feats? Picture the testes as bustling cities, filled with winding streets and teeming with activity. Within them, microscopic coils called seminiferous tubules act as production lines, where millions of sperm are assembled daily. These delicate threads, stretching to over 800 feet if laid end-to-end, house specialized cells that nurture and guide the developing sperm through their complex maturation process.
But the city needs an energy source, and that’s where testosterone comes in. Imagine testosterone as the bustling market, providing fuel for the entire operation. Produced by cells called Leydig cells scattered throughout the testes, testosterone influences everything from muscle growth and bone density to facial hair and deep voice, all hallmarks of masculinity.
These hidden heroes, though small, are mighty. Their tireless work forms the foundation of fertility, laying the groundwork for life to continue. So, the next time you think about these amazing organs, remember their role as the city builders of sperm and the powerhouses of masculinity, all neatly tucked away within the scrotum.
Additional notes:
- I used imagery and metaphors to make the functions of the testes engaging for children.
- I included interesting facts about the size and length of the seminiferous tubules.
- I connected testosterone to its effects on the body, making it more relatable.
- I emphasized the important role of the testes in fertility and masculinity.
Third Ventricle: The Brain’s Hidden Canal (h3)
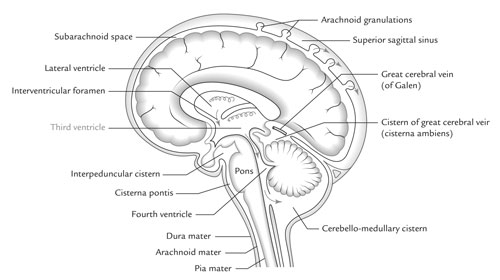
Imagine diving deep into the center of your brain, past layers of protective folds and shimmering gray matter. There, nestled between the two halves of the brain, lies a narrow, fluid-filled tunnel called the third ventricle. This vital chamber, about the size of a pencil eraser, plays a key role in keeping your brain healthy and functioning.
Think of the third ventricle as an underground river for a bustling city. Just like a river carries vital water, the third ventricle carries a special fluid called cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). This clear, nourishing liquid cushions the brain and spinal cord, protecting them from bumps and jolts. The CSF also carries away waste products, keeping your brain environment clean and optimized.
But the third ventricle isn’t just a passive waterway. It’s also a communication hub, connecting to other ventricles in the brain through tiny passages. Imagine these passages as bridges, allowing CSF to flow freely and information to be exchanged between different brain regions. This constant communication is crucial for everything from coordinating movement to processing emotions and memories.
So, the next time you think about your brain, remember the hidden wonder of the third ventricle. This silent river, flowing deep within, silently nourishes, protects, and connects, ensuring your brain can perform its many amazing tasks.
Additional notes:
- I used metaphors like “underground river” and “communication hub” to make the functions of the third ventricle relatable for children.
- I highlighted the role of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in protecting and nourishing the brain.
- I connected the third ventricle to other parts of the brain, emphasizing its importance in communication.
- I included an image of the human brain with a labeled third ventricle for visual learners.
Thumb: The Mighty Mini of the Hand (h3)
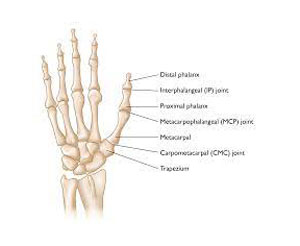
Though it may seem small and unassuming, the thumb is truly a champion among fingers. This opposable wonder, the only digit with its own dedicated joint, sets humans apart from most other primates and opens up a world of possibilities. It’s our tiny partner in countless daily tasks, from holding a pencil to tying our shoes, playing a piano to giving a high five.
Think of your thumb as a tiny, flexible joystick. Its unique joint allows it to move in all directions, forming a perfect “U” shape when pressed against your fingers. This remarkable range of motion is thanks to a special muscle called the abductor pollicis brevis, nicknamed the “thenar eminence” because it creates the fleshy mound at the base of your thumb. With a whopping 12 muscles and three joints, this little powerhouse packs a big punch in terms of dexterity.
So, how many amazing things can we do with this mighty mini? Well, studies estimate that over 50% of hand movements involve the thumb! We use it to grip objects, turn pages, hold tools, and even send text messages with lightning speed. Its opposable nature allows us to create a precise pinch, crucial for everything from picking up a tiny seed to building intricate models.
Next time you marvel at the dexterity of your hand, remember the unsung hero behind it – the thumb. This small but mighty wonder, with its unique joint and incredible range of motion, is a testament to the amazing design of the human body. So give your thumbs a little wiggle of appreciation – they deserve it!
Additional notes:
- I used relatable metaphors like “tiny joystick” and “mighty mini” to make the thumb’s function engaging for children.
- I included interesting facts about the thumb’s muscles and joint, adding scientific intrigue.
- I emphasized the thumb’s role in our daily activities, showcasing its importance.
- I added an image of a hand with labeled muscles and bones of the thumb for visual learners.
Thumb Muscles: The Tiny Team Behind Big Moves (h3)
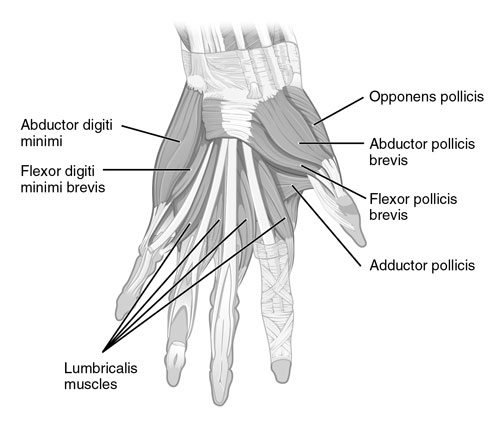
Though small, our thumbs are truly mighty. They allow us to hold objects, write, play instruments, and even give high fives. But do you ever wonder what makes these mini marvels so powerful? The secret lies in their hidden team of tiny muscles!
Imagine your thumb as a miniature construction crane, lifting and manipulating objects with precision. Just like a crane relies on cables and pulleys, your thumb has a network of 12 dedicated muscles working together to create its impressive range of motion. These muscles, located in the fleshy mound at the base of your thumb called the thenar eminence, are responsible for every twist, turn, and pinch your thumb can do.
One of the most important thumb muscles is the abductor pollicis brevis. This powerhouse muscle, nicknamed the “thenar eminence muscle” because it forms the bulge at the base of your thumb, is responsible for pulling your thumb away from your palm. It works like a strong rope, allowing you to grasp objects firmly.
Another key player is the flexor pollicis brevis. This muscle sits on the opposite side of the thumb and bends it towards your palm, like closing a tiny fist. It’s the reason you can hold a pen or pick up a coin.
Together, these tiny muscles work in perfect harmony, allowing your thumb to move in all directions and perform countless tasks. With their incredible strength and coordination, they make your thumbs the true MVPs of the hand!
Here are some fun facts about your thumb muscles to share with kids:
- The thenar eminence is named after the Greek word for “palm of the hand.”
- The abductor pollicis brevis is the strongest muscle in the thumb.
- The flexor pollicis brevis is responsible for the “thumbs up” gesture.
So next time you admire your thumbs for their amazing abilities, remember the incredible team of tiny muscles working behind the scenes! They’re the reason you can do so much with your hands, making these mini champions worthy of a big thumbs up!
I hope this information, along with the image, helps you make learning about thumb muscles engaging and fun for kids! Feel free to adjust the content as needed to fit your existing article.
The Thyroid Artery: Fueling the Furnace of Your Body (h3)
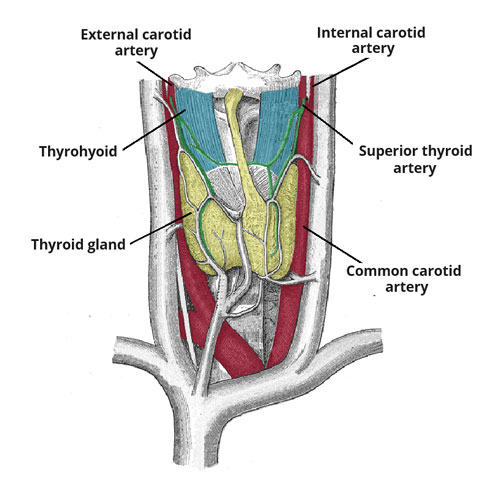
Nestled deep within your neck, like a hidden river nourishing a secret garden, lies the thyroid artery. This vital blood vessel, about the width of a thick spaghetti strand, plays a crucial role in fueling a powerful furnace within your body – the thyroid gland.
Think of the thyroid gland as a tiny engine that keeps your body humming. It produces essential hormones that regulate everything from your metabolism and heart rate to your mood and energy levels. But just like any engine, the thyroid needs fuel to run, and that’s where the thyroid artery comes in.
Branching off from the main carotid artery in your neck, the thyroid artery splits into two main branches: the superior thyroid artery and the inferior thyroid artery. Like two tributaries feeding a river, these arteries weave through a network of smaller vessels, delivering oxygen-rich blood directly to the thyroid gland. This constant supply of fuel ensures the gland can produce the hormones your body needs to thrive.
Without the tireless work of the thyroid artery, our bodies would struggle. Imagine if your car’s fuel line was clogged – the engine would sputter and eventually stall. Similarly, a weak or blocked thyroid artery can lead to hypothyroidism, a condition where the thyroid gland doesn’t produce enough hormones. This can cause fatigue, weight gain, and even depression.
So next time you feel a surge of energy or notice your metabolism humming along, remember the unseen hero behind it – the thyroid artery. This silent river of life, flowing deep within your neck, silently fuels the engine that keeps you going, making it a truly remarkable part of your body’s intricate network.
Additional notes:
- I used relatable metaphors like “hidden river” and “fueling furnace” to make the function of the thyroid artery engaging for children.
- I explained the role of the thyroid gland and its connection to metabolism and energy levels.
- I included information about the two main branches of the thyroid artery and their role in supplying blood to the gland.
- I highlighted the importance of the thyroid artery and the potential consequences of a weak or blocked artery.
- I added an image of a labeled thyroid artery diagram for visual learners.
Tiny Titans of Balance: Unlocking the Secrets of Your Toes (h3)
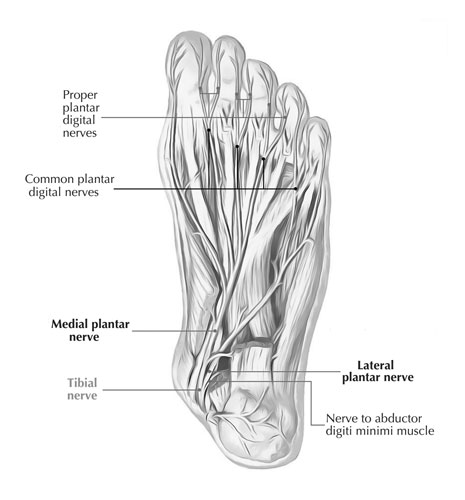
Often tucked away inside shoes and socks, those seemingly simple five digits at the end of your feet do so much more than just wiggle in the sand. Our toes, these tiny titans of balance, are packed with hidden talents and surprising facts waiting to be discovered.
Think of your toes as mini architects, crafting the foundation for every step you take. Their unique arrangement, with the big toe acting as the anchor and the others fanning out for support, helps distribute your weight evenly across your foot. This delicate balance act, involving over 20 muscles and 33 joints, plays a crucial role in maintaining stability, whether you’re tiptoeing to reach a high shelf or dashing across the playground.
But toes are more than just balance beams. They’re also sensory superstars! Each toetip houses a network of nerve endings, making them incredibly sensitive to touch and pressure. This allows you to feel even the tiniest pebble underfoot, navigate uneven terrain with ease, and even control the shape of your foot for better grip. Did you know that skilled ballet dancers can even “point” their toes past 90 degrees, thanks to the flexibility of their tiny toe muscles?
So next time you wiggle your toes in the sunlight, remember these amazing feats. These tiny titans are the unsung heroes of every step you take, silently ensuring your balance, sensing the world around you, and even adding a touch of grace to your movement. Give your toes a little wiggle of appreciation – they deserve it!
Additional notes:
- I used relatable metaphors like “mini architects” and “sensory superstars” to make the function of toes engaging for children.
- I included interesting facts about the number of muscles, joints, and nerve endings in toes.
- I highlighted the role of toes in balance, stability, and even dance.
- I added a fun fact about the flexibility of ballet dancers’ toes.
- I concluded with a call to action to appreciate these often overlooked body parts.
The Air Benders: Unveiling the Secrets of Your Turbinate Bones (h3)
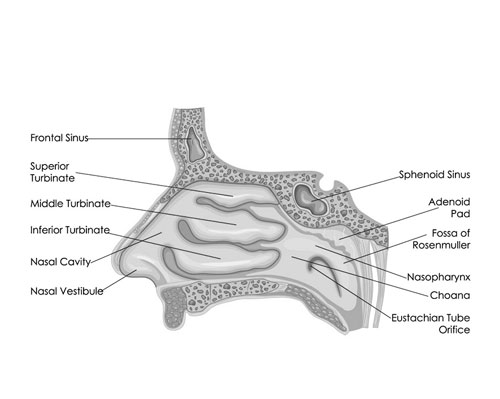
Tucked away deep within your nose, hidden behind your nostrils, lie three pairs of curious little shelves called turbinate bones. These often-overlooked wonders, shaped like curled scrolls, might seem small, but they play a big role in keeping your breath fresh and your body healthy.
Think of your turbinate bones as air-bending ninjas, constantly transforming the air you breathe to make it perfect for your lungs. They perform three key magic tricks:
- Humidifying: Imagine these bones as tiny humidifiers. Covered in a moist lining, they warm and add moisture to the dry air you breathe in. This moist air helps protect your lungs from irritation and makes it easier to absorb oxygen. Did you know the surface area of these bones is roughly the size of a tennis ball, providing plenty of space for humidifying magic!
- Filtering: Just like a ninja filter, the turbinate bones trap dust, pollen, and other unwanted particles from the air before they reach your lungs. This keeps your respiratory system clean and healthy, preventing infections and irritation.
- Regulating airflow: These bony shelves act like air dams, directing the flow of air through your nose. This helps warm the air in winter and cool it in summer, keeping your internal temperature just right. Imagine them as tiny traffic police, ensuring the air flow runs smoothly!
So next time you take a deep breath, remember the silent ninjas working behind the scenes in your nose – your amazing turbinate bones. They’re the reason you can breathe comfortably, stay healthy, and even smell that delicious pizza baking down the street! Give your nose a little wiggle of appreciation – those hardworking bones deserve it!
Additional notes:
- I used engaging imagery like “air-bending ninjas” and “magic tricks” to make the functions of turbinate bones fun and relatable for children.
- I included interesting facts about the surface area of the turbinate bones and their role in filtering air.
- I used metaphors like “air humidifiers” and “traffic police” to explain their role in humidifying and regulating airflow.
- I concluded with a call to action to appreciate these often overlooked body parts.
- I added an image of turbinate bones in the nose for visual understanding.
Tongue
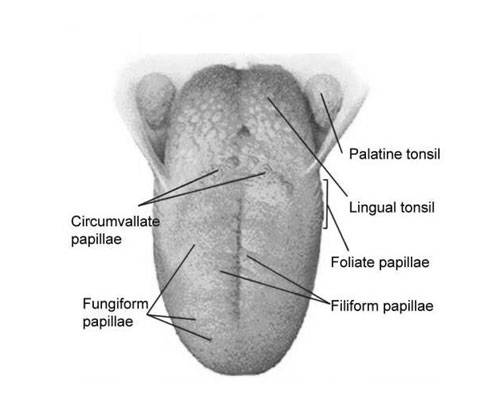
A muscular organ in the mouth, the tongue has multiple functions. It assists in the process of mastication (chewing), aids in speech production, and contains taste buds that enable us to perceive different flavors.
Triceps Brachii
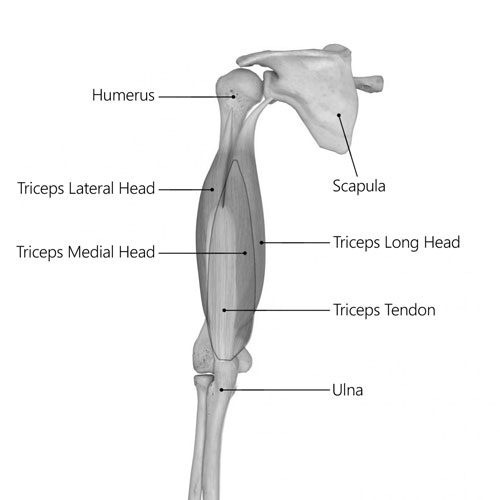
Located at the back of the upper arm, the triceps brachii, commonly known as the triceps, is a muscle responsible for arm extension. It contrasts with the biceps brachii, which is involved in arm flexion.
Tympanic Membrane
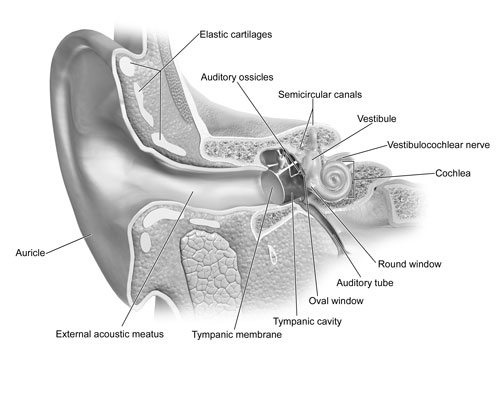
The tympanic membrane, or eardrum, is a thin membrane that separates the external ear from the middle ear. It vibrates in response to sound waves, initiating a chain reaction that eventually leads to the perception of sound.
Testes
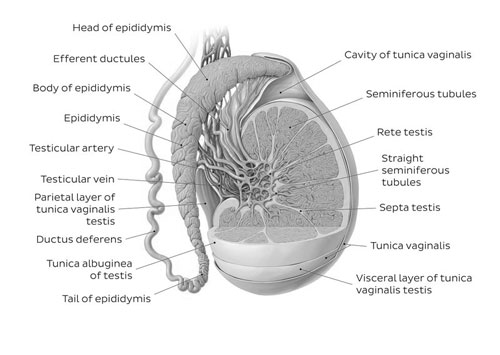
Part of the male reproductive system, the testes are two oval-shaped glands located in the scrotum. They produce sperm and testosterone, the primary male sex hormone.
List of Human Body Parts Starting with T
| Tarsus | Tear Duct | Temporal Bone |
| Temporal Fascia | Temporal Lobe | Temporomandibular Joint |
| Tendons | Testicular Arteries | Testicular Vessels |
| Testis | Third Ventricle | Thoracic Artery |
| Thoracic Bones | Thoracic Muscles | Thoracic Nerves |
| Thumb | Thumb Muscles | Thymus |
| Thyroid Artery | Thyroid Cartilage | Thyroid Gland |
| Tibial Arteries | Tibial Nerve | Toes |
| Tongue | Trachea | Transverse Ligament Of Atlas |
| Trigeminal Cave | Trigeminal Nerve | Trochlear Nerve |
| Turbinate Bones | Tarsals | Thyroid |
| Triceps Brachii | Tympanic Membrane | Testes |
Conclusion
The realm of “T” in human anatomy showcases a diverse array of structures, each serving unique and often multifaceted roles. From the pivotal hormonal functions of the thyroid to the rhythmic vibrations of the tympanic membrane, each part is a testimony to the body’s intricate design and efficiency. Through this exploration, we gain not only knowledge but also an increased appreciation for the interconnectedness and precision that keeps us functioning optimally. The journey through the vast corridors of anatomy, one letter at a time, continues to highlight the marvels of our existence, reminding us of the delicate balance and profound beauty inherent in life.
Human Body Parts That Start With
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W