Forge ahead with us on our continuing expedition through the intricate terrain of human anatomy. This next installment, “Body Parts That Start With F,” is a fascinating exploration into those parts of our bodies that begin with the letter ‘F’. We’ll journey from familiar parts such as the fingers to lesser-known ones like the foramen, bringing light to their function, structure, and unique attributes.
This article serves as a handy resource for students, teachers, or anyone intrigued by the workings of the human body. Whether you’re a medical expert or a curious explorer, we invite you to further your understanding of the human body’s complexity and elegance, one letter at a time.
Human Body Parts That Start With The Letter F
The human body, a remarkable and intricate machine, boasts a wide array of parts that work together to ensure our survival and wellbeing. As we journey through the body alphabetically, we arrive at the letter “F.” Though it may not have the largest repertoire, it certainly designates a number of critical structures in our bodies. This article will focus on those body parts that start with “F,” discussing their structure, function, and the role they play in our overall health.
Femur
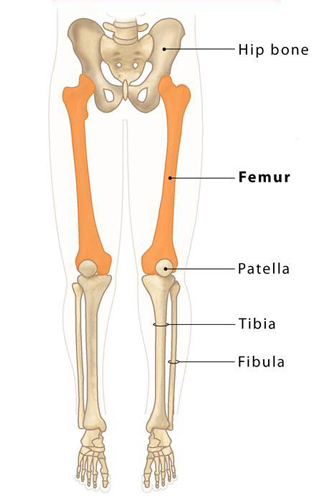
The femur, also known as the thigh bone, is the longest, heaviest, and strongest bone in the human body. Located in the upper leg, the femur connects the hip to the knee, providing structural support and facilitating movement. Its robustness helps it withstand the substantial pressures and stresses involved in activities like walking, running, and jumping.
Fibula
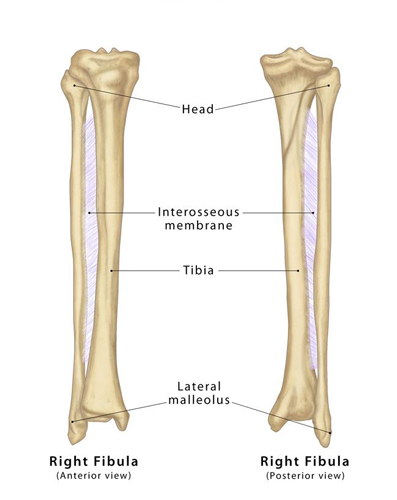
The fibula is the slender bone located in the lower leg, parallel and lateral to the larger tibia (shinbone). Despite being thinner and less critical for bearing weight than its neighbor, the fibula plays a significant role in stabilizing the ankle and supporting the muscles of the lower leg. It also serves as an attachment site for various muscles and ligaments.
Fingers
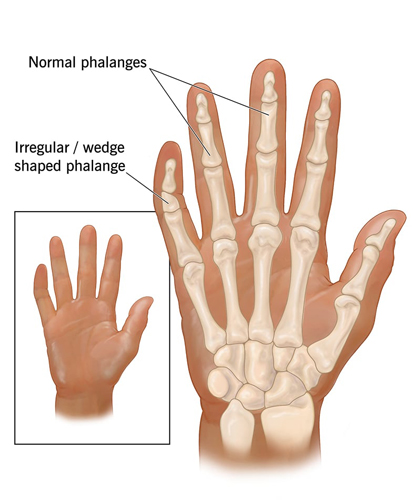
Our fingers are vital structures that provide us with the dexterity to perform a wide array of tasks. From writing and typing to grasping and lifting, fingers play an invaluable role in our daily lives. Each finger, except for the thumb, consists of three phalanges (bones) – proximal, middle, and distal – joined by two interphalangeal joints. The thumb, with its unique opposability, has two phalanges and one interphalangeal joint.
Frontal Lobe
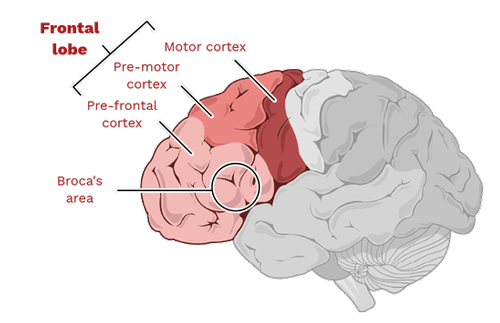
The frontal lobe is the largest of the brain’s four main lobes, located at the front of the brain. It’s involved in numerous higher cognitive functions, including decision-making, problem-solving, consciousness, and the majority of our voluntary movement. It’s also home to Broca’s area, which is critical for speech and language production.
Foot
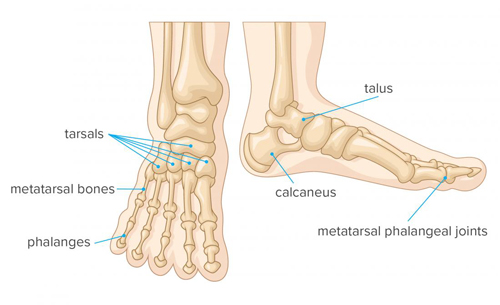
The foot, a complex structure at the lower end of the leg, plays several key roles, including bearing weight, providing balance, and enabling locomotion. It consists of 26 bones, 33 joints, and more than a hundred muscles, tendons, and ligaments. The foot’s arch structure gives it the strength and flexibility to adapt to various surfaces and absorb shock during movement.
Follicles
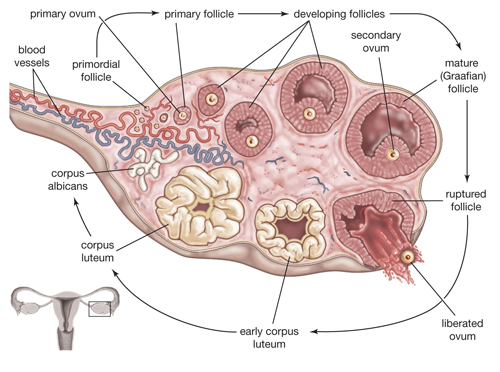
In the context of the human body, follicles are small sac-like structures that have various functions depending on their location. Hair follicles, for example, are tiny pouches in our skin that produce hair. On the other hand, ovarian follicles, found in the ovaries of females, are involved in the maturation and release of eggs for reproduction.
Fallopian Tubes
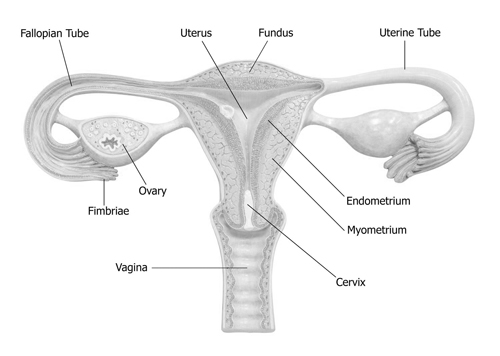
In the female reproductive system, the fallopian tubes are two slender tubes that serve as a pathway for ova from the ovaries to the uterus. Besides transportation, the fallopian tubes are the typical site for fertilization, where the sperm meets and fertilizes the egg.
Facial Bones: The Foundation of Our Expressions
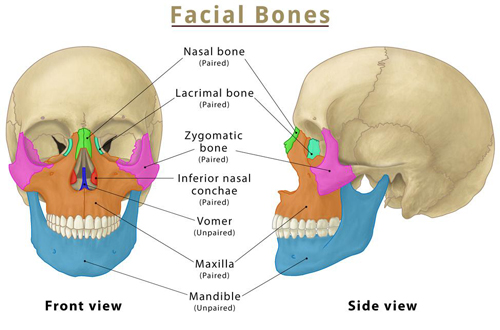
Imagine a sturdy yet intricate mask shaping our faces – that’s the magic of the facial bones. These 14 bones form the foundation of our faces, providing structure, supporting vital organs, and enabling us to express emotions through subtle movements.
- Bone Brigade: The 14 facial bones include:
- Maxilla: Upper jawbone, supporting the upper teeth and forming the cheeks.
- Mandible: Lower jawbone, housing the lower teeth and enabling chewing and speech.
- Nasal Bones: Form the bridge of the nose, providing structure and influencing scent detection.
- Zygomatic Bones: Cheekbones, shaping the face and aiding in jaw movement.
- Frontal Bone: Forehead bone, protecting the brain and contributing to facial expression.
- Other Essential Bones: Sphenoid, ethmoid, palatine, lacrimal, vomer, and inferior nasal conchae complete the set, offering support and playing specialized functions.
- Expression Architects: The unique arrangement of facial bones allows for the subtle movements that create our expressions. Eyebrows raise and furrow due to the frontal bone and surrounding muscles, while smiles and frowns involve the interplay of maxilla, mandible, and surrounding muscles.
- Protecting the Precious: Facial bones provide a protective shield for vital organs like the eyes, nose, and brain. Their strong structure absorbs impact and shields delicate structures from harm.
Flexor Muscles: Bending Masters of the Body
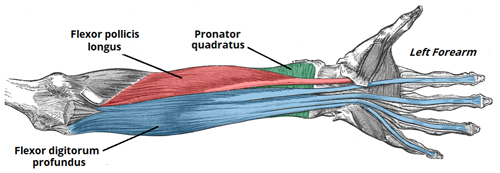
Imagine a hidden network of strings pulling your bones to create movement – that’s the wonder of the flexor muscles. These hardworking heroes bend your limbs, bring your body closer, and enable countless everyday actions.
- Muscle Mashup: There are numerous flexor muscles throughout the body, each with a specific function:
- Arm Flexors: Biceps brachii bends the elbow, while brachialis and other arm flexors assist in various movements.
- Leg Flexors: Hamstrings bend the knee, while hip flexors like the psoas major flex the hip joint.
- Neck Flexors: Sternocleidomastoid and other neck flexors tilt the head forward and side to side.
- Hand and Finger Flexors: Numerous muscles in the forearm and hand control finger and wrist flexion, enabling grasping, holding, and intricate hand movements.
- Power and Precision: Flexor muscles work in coordination with extensor muscles (responsible for straightening) to provide balanced movement and control. Their strength allows us to lift objects, climb stairs, run, and perform countless other activities.
- Maintaining Movement: Stretching regularly, engaging in strengthening exercises, and practicing good posture can help prevent flexor muscle tightness and keep your body moving smoothly.
Foot Ligaments: Silent Supporters of Every Step
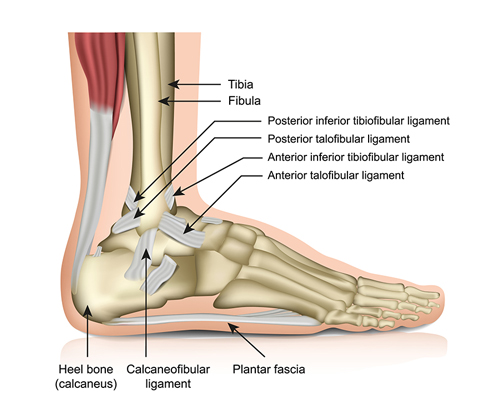
Imagine invisible bands holding your foot bones together and providing stability – that’s the role of the foot ligaments. These unsung heroes play a crucial role in supporting our weight, enabling balance, and absorbing shock during movement.
- Ligament Latticework: There are over 30 ligaments in the foot, connecting various bones and providing stability:
- Ankle Ligaments: Medial and lateral collateral ligaments stabilize the ankle joint, preventing excessive inward and outward rolling.
- Tarsal Ligaments: Connect the tarsal bones of the midfoot, ensuring proper alignment and weight distribution.
- Metatarsal Ligaments: Stabilize the metatarsals of the forefoot, providing support for push-off during walking and running.
- Shock Absorbers: Foot ligaments act as shock absorbers, distributing pressure and protecting the bones and joints from excessive stress during activities like walking, running, and jumping.
- Balance Buddies: Foot ligaments work in conjunction with muscles and tendons to maintain balance and coordination. They help prevent excessive ankle rolling and ensure proper positioning of the foot during movement.
Forearm: Powerhouse of the Hand
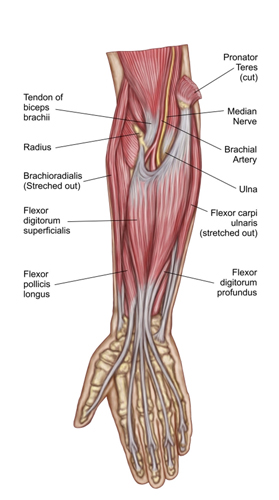
Imagine a muscular bridge connecting your hand to your elbow – that’s the remarkable forearm. This compact powerhouse houses a network of muscles and bones that enable us to grasp, twist, and manipulate objects with remarkable precision and strength.
- Muscle Mashup: Two main groups of muscles dominate the forearm:
- Extensors: Located on the back of the forearm, these muscles straighten the fingers and wrist, allowing us to push, pull, and extend our reach. Examples include the triceps brachii and extensor carpi ulnaris.
- Flexors: Situated on the front of the forearm, these muscles bend the fingers and wrist, enabling us to grasp, hold, and perform intricate hand movements. Examples include the biceps brachii and flexor carpi radialis.
- Bone Builders: Two sturdy bones, the radius and ulna, provide the framework for the forearm. They rotate around each other, allowing for pronation (turning the palm down) and supination (turning the palm up). This rotational ability is crucial for various everyday tasks like hammering, writing, and opening doors.
- Strength and Dexterity: The combination of powerful muscles and flexible bones allows the forearm to perform a wide range of movements with remarkable control. From delicate typing to forceful lifting, the forearm is a versatile tool that plays a vital role in our daily activities.
Foramen Magnum: Gateway to the Brain
Imagine a tiny hole at the base of your skull, allowing your brain to connect with your spinal cord – that’s the foramen magnum. This crucial gateway serves as the main passage for vital nerves and blood vessels, ensuring communication and nourishment for our central nervous system.
- Skull Sanctuary: Located at the junction of the occipital bone and the first cervical vertebra (atlas), the foramen magnum is roughly the size of a quarter. It provides a secure opening while protecting the delicate brainstem from external damage.
- Neural Network: Numerous vital structures pass through the foramen magnum:
- Brainstem: Connects the brain to the spinal cord, relaying sensory information and motor commands.
- Spinal Cord: Descends from the brainstem and carries nerves throughout the body, controlling movement and relaying sensory information.
- Blood Vessels: Arteries supply the brain with oxygen-rich blood, while veins drain deoxygenated blood back to the heart.
- Protecting the Precious: The foramen magnum is surrounded by strong muscles and ligaments that support the head and maintain proper alignment of the brain and spinal cord. This robust protection is crucial for the optimal functioning of our nervous system.
Fossa Ovale: Cardiac Check Valve
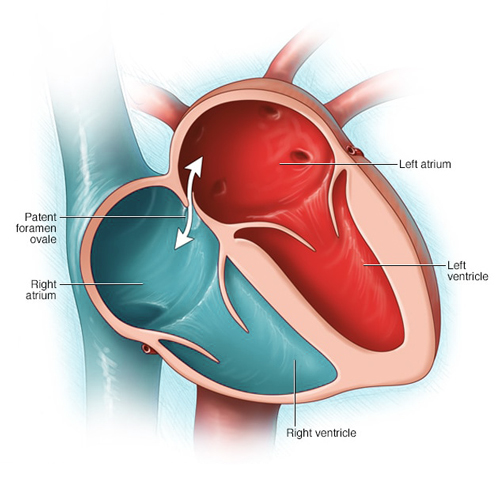
Imagine a tiny flap within your heart preventing blood from flowing backward – that’s the remarkable fossa ovale. This crucial structure, a remnant of fetal circulation, plays a vital role in ensuring proper blood flow within the heart.
- Embryonic Echo: During fetal development, the fossa ovale allows oxygenated blood to bypass the lungs and circulate directly to the body. After birth, this opening naturally closes, and blood follows the normal circulatory path through the lungs.
- Safety Valve: In some individuals, the fossa ovale may not completely close, leaving a small opening. This “patent foramen ovale” is usually harmless and doesn’t require medical intervention. However, in certain cases, it can allow blood clots or bubbles to bypass the lungs, requiring medical attention.
- Heart Harmony: The fossa ovale, even if closed, plays a crucial role in maintaining proper blood flow within the heart. It contributes to the coordinated movement of the heart chambers, ensuring efficient pumping and optimal circulation.
Fovea
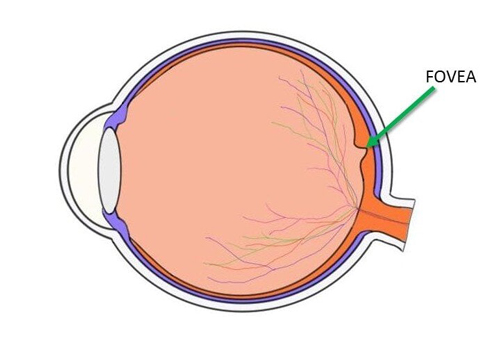
The fovea, located in the center of the macula in the retina of the eye, is responsible for sharp central vision (also called foveal vision), which is necessary for activities where visual detail is important, such as reading and driving. The fovea has a high concentration of cone cells, which are responsible for detecting color and fine detail.
Fat (Adipose Tissue)
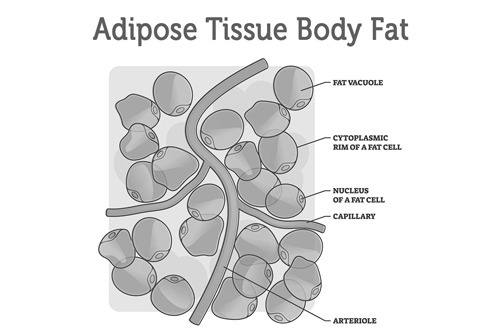
While fat or adipose tissue is often associated negatively due to its relation to obesity, it plays several vital roles in the body. This specialized tissue stores energy, insulates the body, and protects vital organs. It also produces and releases hormones that regulate metabolism and appetite. Adipose tissue can be found subcutaneously (under the skin) and around internal organs (visceral fat).
List of Human Body Parts Starting with F
| Facial Bones | Facial Muscles | Facial Nerve |
| Female Reproductive Organs | Femur | Fibula |
| Fingers | Flexor Muscles | Flexor Muscles Of Front Of Neck |
| Foot | Foot Ligaments | Foot Muscles |
| Foramen Magnum | Foramen Magnum, From Above | Foramen Ovale |
| Forearm | Fossa Ovale | Fourth Ventricle |
| Frontal Sinus | Frontal Sinus, Opening | Fat (Adipose Tissue) |
| Fovea | Fallopian Tubes | Frontal Lobe |
Conclusion
This exploration of body parts beginning with “F” reveals an intriguing mix of structures essential for our daily functioning and survival. From the femur, crucial for movement, to the frontal lobe, instrumental in our cognitive functions, each body part plays a unique and crucial role. As we delve deeper into the human body and its many parts, we continue to discover the tremendous complexity and marvel that is human anatomy.
Human Body Parts That Start With
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W