The human body, with its myriad components and intricate design, is an awe-inspiring marvel of biological engineering. As we navigate this vast anatomical landscape alphabetically, each letter uncovers a fresh chapter of discovery, revealing the delicate balance and interdependence of our bodily structures. The letter ‘P’ introduces us to a constellation of parts that span the spectrum from the superficial to the deeply seated, some constantly in motion while others maintain a stoic stillness.
This article embarks on an enlightening journey through the ‘P’-initiated body parts, diving deep into their anatomy, physiology, and the pivotal roles they play in our daily lives. From the pulsating power of the heart’s pump to the protective shield of our patella, prepare to immerse yourself in the wonders of the human body that begin with the letter “P.”
Human Body Parts That Start With The Letter P
The complex tapestry of the human body is marked by a multitude of structures, each contributing distinctively to our overall health and functionality. In our ongoing series exploring the body alphabetically, we’ve now reached the letter “P.” This section is particularly abundant, showcasing an array of organs, tissues, and systems that are fundamental to our existence. This comprehensive exploration delves into the body parts starting with “P,” elucidating their functions, characteristics, and importance in the broader scope of human physiology.
Pancreas
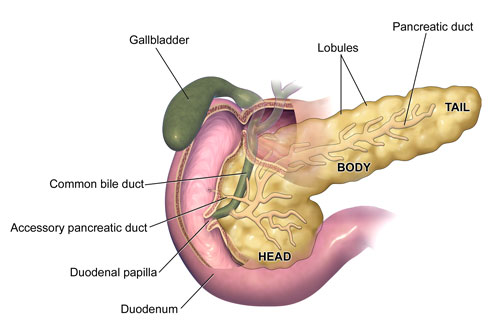
Nestled deep within the abdominal cavity, the pancreas is a vital organ with dual functionality. It plays a pivotal role in the digestive system by secreting digestive enzymes, and in the endocrine system by producing hormones like insulin and glucagon. These hormones are quintessential in regulating blood sugar levels.
Parietal Lobe
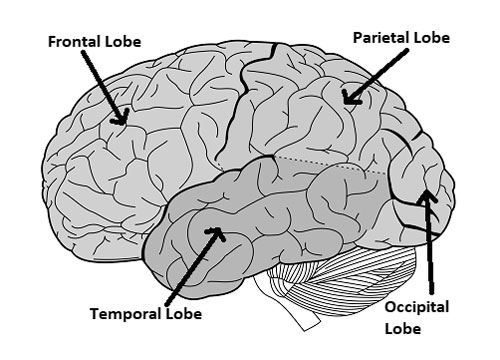
The human brain, a marvel of nature’s engineering, is segmented into different lobes, each with its unique responsibility. The parietal lobe, situated at the upper back part of the cortex, is crucial for sensory integration. It interprets signals from the body, including touch, temperature, and taste, aiding in spatial awareness and coordination.
Patella
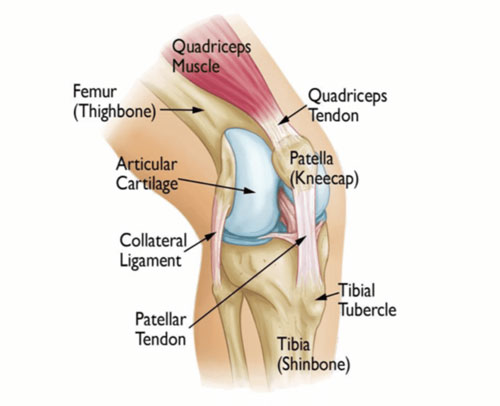
Commonly known as the kneecap, the patella is a triangular bone located at the front of the knee joint. It protects the knee and provides leverage to the quadriceps muscles, facilitating leg extension.
Phalanges
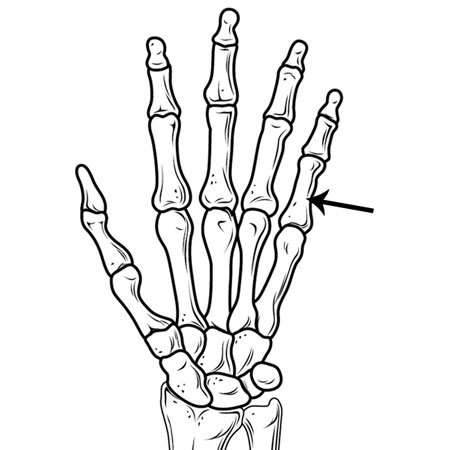
Extending the hands and feet are the phalanges – the bones of the fingers and toes. Each hand and foot possesses 14 phalanges, divided as three for each finger and toe, except for the thumb and big toe, which have two each. These bones provide dexterity and aid in tactile sensation.
Pineal Gland
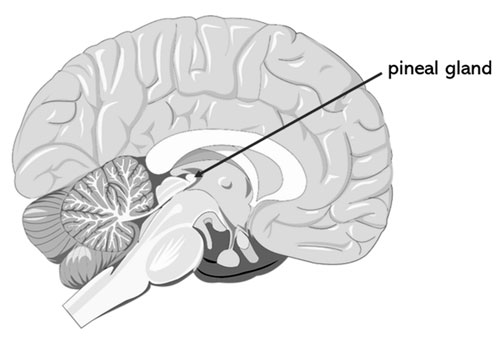
Tucked within the brain’s depths is the pineal gland, a tiny, pinecone-shaped endocrine organ. It’s most known for secreting melatonin, a hormone responsible for regulating sleep-wake cycles.
Pituitary Gland
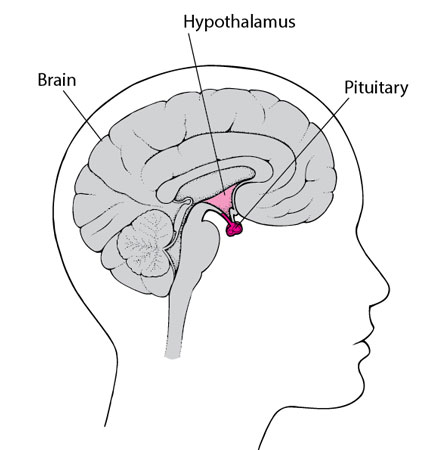
Often referred to as the “master gland,” the pituitary is a pea-sized organ located at the base of the brain. It plays a central role in the endocrine system, producing a variety of hormones that govern other glands and influence numerous body functions, from growth and reproduction to metabolism.
Plasma
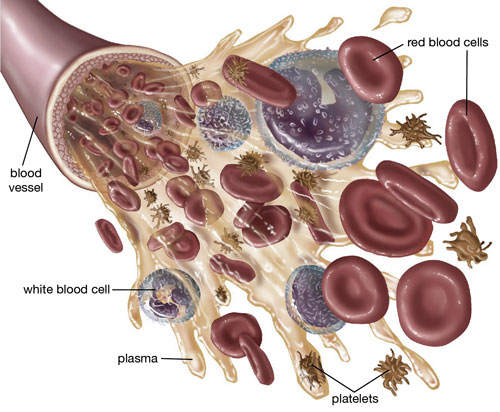
Blood, the life-sustaining fluid coursing through our veins, is composed of various components. Plasma is the liquid portion, making up about 55% of total blood volume. It carries cells, nutrients, hormones, and waste products throughout the body.
Palmar Arch: Powerhouse in your Palm
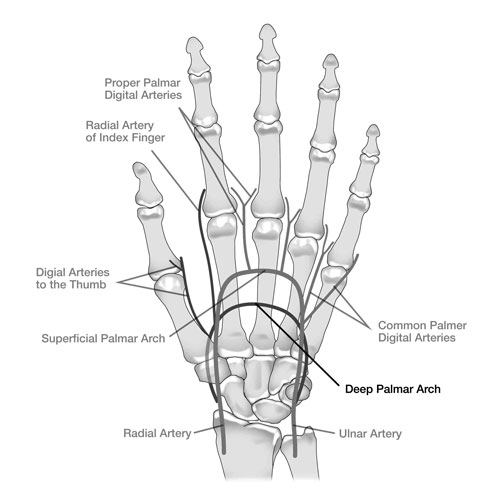
Ever wondered how blood reaches every nook and cranny of your hand, allowing you to grasp, pinch, and write with finesse? Enter the Palmar Arch, a network of arteries forming a bridge across the base of your hand. This intricate arch, formed by two main arteries (radial and ulnar), ensures a steady flow of blood to your fingers, powering their incredible dexterity.
Think of the Palmar Arch as a city highway system. The radial artery enters like a major freeway, branching out into smaller roads (arteries) supplying the thumb and radial side of the hand. Meanwhile, the ulnar artery acts as another major route, feeding the ulnar side and little finger. These two pathways then interconnect like bridges, forming the arch and guaranteeing blood supply even if one pathway gets blocked.
The Palmar Arch is crucial for daily life. Its intricate design allows for delicate finger movements, from tying shoelaces to playing a musical instrument. Its importance shines through in professions like hand therapy, where understanding the arch’s anatomy is key to treating injuries and restoring hand function.
Papillary Muscles: Tiny Titans of the Heart
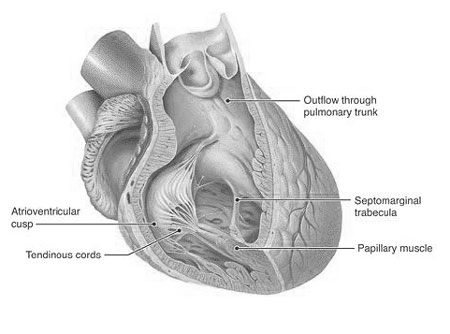
Hidden within the heart’s chambers lie the Papillary Muscles, muscular projections acting as miniature gatekeepers. These unassuming structures play a vital role in ensuring your heart pumps blood efficiently throughout your body.
Imagine the heart as a two-story house. The Papillary Muscles reside on the lower floor (ventricles), attached to the heart valves like tiny strings. When the ventricles contract to pump blood, these muscles pull the valve flaps upwards, preventing them from bulging back and leaking blood backwards. It’s like miniature tug-of-war teams ensuring smooth one-way blood flow.
There are two sets of Papillary Muscles: one for each of the heart’s main valves (mitral and tricuspid). Each set branches out like a tree, with smaller muscle fibers reaching different parts of the valve flaps. This intricate network ensures even distribution of pulling force, preventing any weak spots that could lead to leakage.
Understanding the Papillary Muscles helps us appreciate the heart’s incredible complexity. These tiny titans, often overlooked, are essential for maintaining healthy blood flow and keeping our bodies functioning properly.
Pelvic Veins: A Network Beneath the Belt
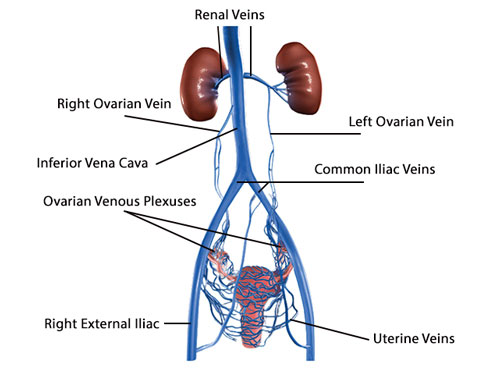
Deep within the pelvis, below the belly button, lies a crucial venous network known as the Pelvic Veins. These hidden channels play a vital role in blood circulation, particularly for the reproductive organs and lower extremities.
Imagine the Pelvic Veins as a complex underground drainage system. Blood from the legs, bladder, intestines, and reproductive organs flows into these veins, eventually draining back to the heart. The system includes deep and superficial veins, interconnected like underground tributaries, ensuring efficient blood return.
Maintaining healthy Pelvic Veins is essential for both men and women. In women, they play a vital role in supporting the baby and uterus during pregnancy. Blockages in these veins can lead to various conditions, including varicose veins and pelvic congestion syndrome. Therefore, promoting good circulation through exercise and healthy lifestyle choices is crucial for pelvic health.
By understanding the Palmar Arch, Papillary Muscles, and Pelvic Veins, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate workings of the human body. These seemingly small or hidden structures work in perfect harmony to maintain our health and well-being, reminding us of the body’s amazing design and resilience.
Perineal Body: The Hidden Bridge Builder
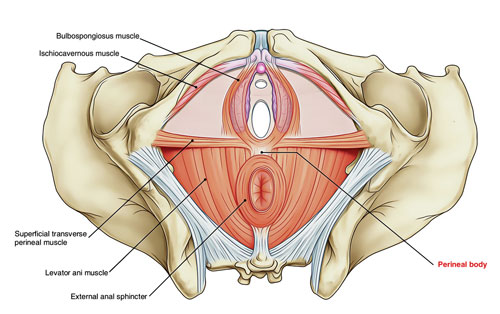
Tucked away between the legs, where the thighs meet, lies the Perineal Body, a hidden powerhouse often unnoticed yet crucial for everyday functions. This muscular bridge connects various muscles and tissues, providing support and stability for crucial functions like childbirth, bowel movements, and urinary control.
Imagine the Perineal Body as a suspension bridge holding up a vital highway. It’s formed by layers of muscles and collagen, creating a firm sling-like structure. This bridge supports pelvic organs like the bladder and rectum, preventing them from prolapsing downwards. It also plays a vital role in childbirth, stretching and widening to allow the baby’s passage.
Strengthening the Perineal Body through Kegel exercises can offer numerous benefits. Improved muscle tone enhances bladder and bowel control, preventing incontinence. For pregnant women, strong perineal muscles can ease childbirth and reduce the risk of tearing. In men, a healthy Perineal Body can contribute to better erectile function.
Phrenic Nerve: The Conductor of Breath
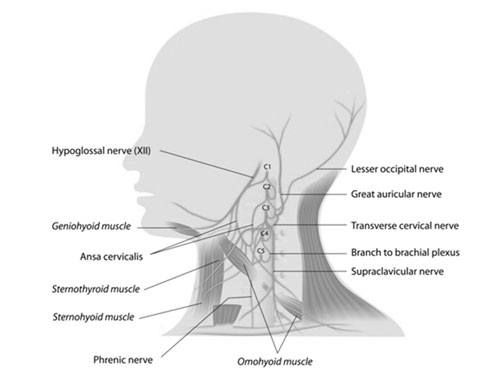
Deep within the chest, orchestrating every inhale and exhale, lies the Phrenic Nerve, the master conductor of our breath. This pair of nerves, originating from the spinal cord, control the diaphragm, the main muscle responsible for breathing.
Think of the Phrenic Nerve as a pair of wires connecting the brain to the diaphragm, like the cables linking a conductor to the orchestra. When the brain sends a signal through the Phrenic Nerve, the diaphragm contracts, pulling down on the ribs and lungs, creating a vacuum that draws air in. To exhale, the nerve relaxes, allowing the diaphragm and lungs to recoil and push air out.
Understanding the Phrenic Nerve’s role can help us appreciate the amazingness of breathing. Every minute, we take around 18 breaths, thanks to the tireless work of these nerves. They also play a crucial role in activities like coughing, sneezing, and even singing!
Pituitary Fossa: The Tiny Throne of Hormones
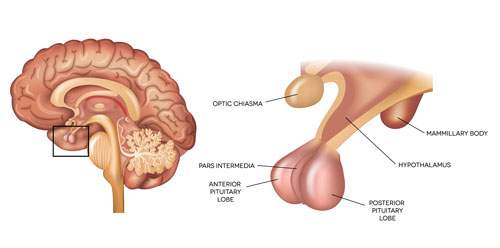
Nestled deep within the brain, protected by bone, sits the Pituitary Fossa, a pea-sized cavity housing the mighty pituitary gland. This tiny “master gland” releases hormones that regulate crucial bodily functions, making it the conductor of our internal orchestra.
Imagine the Pituitary Fossa as a throne room within the brain, where the pituitary gland sits like a king, sending out messengers (hormones) to control various kingdoms (body functions). Hormones regulate growth, metabolism, reproduction, and even mood, orchestrating a complex symphony within us.
The pituitary gland’s importance is reflected in its complex blood supply. Tiny arteries directly from the heart nourish this vital organ, ensuring it has the resources to fulfill its critical role. Understanding the Pituitary Fossa and its resident master gland helps us appreciate the intricate communication systems within our bodies, where even the smallest structures hold immense power.
Plantar Muscles: Movers and Shakers of the Sole
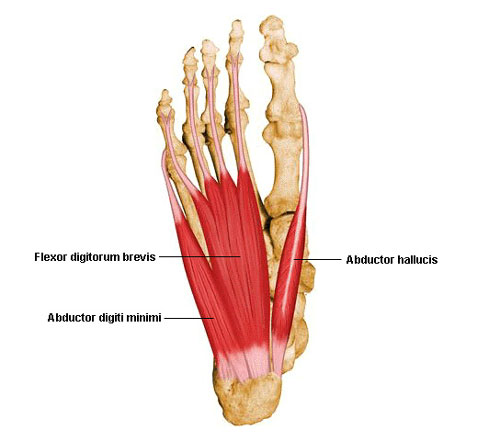
Beneath your feet, hidden behind the tough plantar fascia, lies a powerhouse of muscles known as the Plantar Muscles. These hardworking heroes control all the intricate movements of your toes and foot, powering everything from walking and running to dancing and balancing.
Imagine the Plantar Muscles as a bustling city beneath your feet. There are two main layers: the superficial layer with muscles like the abductor hallucis (moves your big toe outwards) and flexor digitorum brevis (bends your toes), and the deeper layer with the quadratus plantae (stabilizes the arches) and lumbricals (fine-tune toe movements). These muscles work together like a well-coordinated team, pulling tendons and bones to create every action your foot performs.
Did you know? We have 20 Plantar Muscles in each foot, more than any other part of the body except the hands! Keeping these muscles strong and flexible through exercises like toe raises and foot stretches is crucial for maintaining good balance, preventing injuries, and ensuring graceful movement throughout your life.
Pulmonary Artery: The Highway to the Lungs
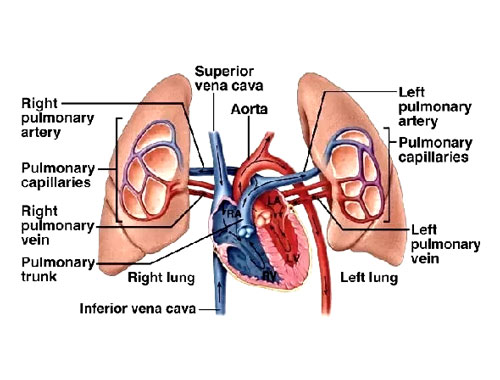
Deep within your chest, carrying oxygen-rich blood from your heart to your lungs, lies the mighty Pulmonary Artery. This vital vessel, unlike most arteries, carries blood away from the heart instead of to it. Think of it as a highway taking traffic – in this case, oxygen – to its destination.
The Pulmonary Artery splits like a fork in the road, sending one branch to each lung. Inside the lungs, these branches further divide into smaller and smaller vessels, forming delicate capillaries that surround tiny air sacs. This intricate network allows oxygen to diffuse from the air sacs into the bloodstream, while carbon dioxide waste gas travels the opposite way, ready to be exhaled.
Did you know? The right branch of the Pulmonary Artery is slightly wider than the left, as the right lung receives slightly more blood flow. Every time you take a breath, around 5 liters of blood travels through the Pulmonary Artery to pick up fresh oxygen and release waste!
Pulmonary Veins: Return to the Heart
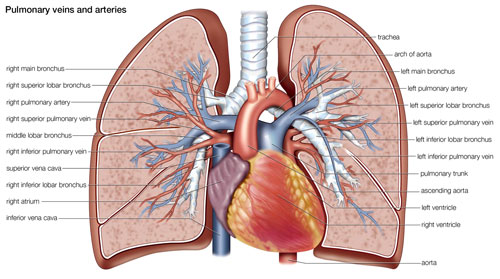
Once oxygen is picked up in the lungs, it’s time to head back to the heart! This essential journey is taken by the Pulmonary Veins, four vessels (two from each lung) that carry oxygen-rich blood back to the left atrium of the heart. Think of them as return lanes on the oxygen highway, bringing the vital fuel your body needs to function.
Unlike most veins, which carry deoxygenated blood, the Pulmonary Veins are the only veins that carry oxygen-rich blood. These thin-walled vessels are under low pressure, as the heart needs minimal effort to suck the blood back in. Once in the left atrium, the oxygen-rich blood is ready to be pumped throughout the body by the powerful left ventricle.
Did you know? The four Pulmonary Veins converge into a single vessel before entering the left atrium, making it the only chamber of the heart to receive blood from only one source. This unique design ensures efficient circulation of oxygen-rich blood, keeping your body running like a well-oiled machine.
Pterygoid Muscles: Powerful Players in Your Jaw
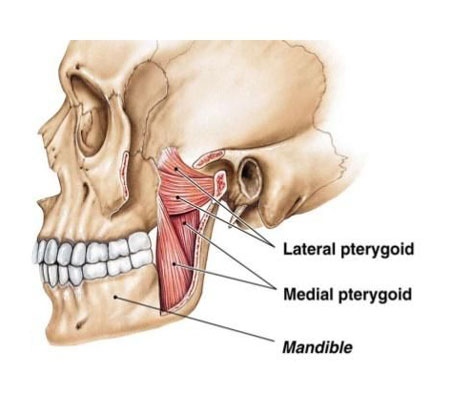
Deep within your skull, near your jaw and cheeks, reside two sets of remarkable muscles known as the Pterygoid Muscles. These hidden heroes play a crucial role in every bite, chew, and swallow, powering the incredible movements of your jaw.
Imagine the Pterygoid Muscles as a pair of tug-of-war teams, one on each side of your jaw. The lateral pterygoid muscles act like strong ropes, pulling your jaw forward when you bite or open your mouth wide. Think of them as the “openers” of your jaw joint. Meanwhile, the medial pterygoid muscles work like powerful springs, pulling your jaw upwards and sideways to grind and crush food. They’re the “closers” of your jaw joint.
Did you know? The Pterygoid Muscles are incredibly strong! The medial pterygoid alone can generate a force of over 100 pounds, allowing you to chew even the toughest of foods. Keeping these muscles healthy through balanced diet and jaw exercises can prevent jaw pain and ensure smooth chewing action throughout your life.
Psoas Major Muscle: Your Core Powerhouse
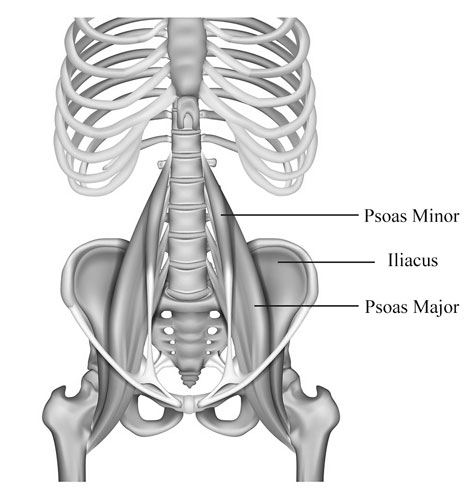
Tucked deep within your abdomen, hidden behind your intestines, lies the Psoas Major Muscle. This powerful “hip flexor” plays a vital role in everyday movements, from walking and running to standing up and climbing stairs. Think of it as a hidden engine driving your lower body.
Imagine the Psoas Major Muscle as a thick band running from your lower spine to your thigh bone. It connects your torso to your legs, allowing you to bend your hip and flex your leg. When you walk, it pulls your leg forward with each step. When you run, it helps propel you forward with powerful strides. This versatile muscle even aids in maintaining good posture and stabilizing your spine.
Did you know? The Psoas Major Muscle is often called the “muscle of the soul” because of its connection to the diaphragm and its influence on posture and breathing. Keeping this core muscle strong and flexible through exercises like lunges and planks can improve your posture, prevent back pain, and enhance your overall athletic performance.
Peritoneum: Your Body’s Inner Lining
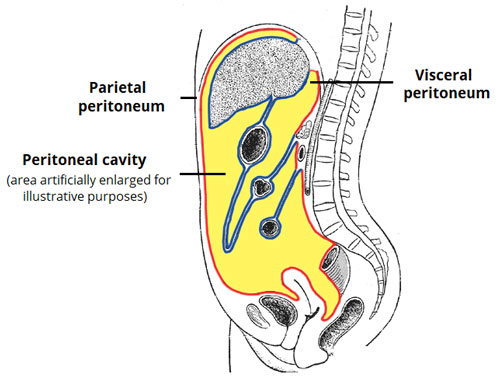
Imagine your body as a house, and the Peritoneum as the wallpaper lining the walls and covering the furniture. This thin, slippery membrane blankets most of your internal organs, providing support, lubrication, and protection. It acts like a delicate second skin for your abdominal and pelvic cavities.
The Peritoneum has two main layers: the visceral layer clinging directly to organs like the intestines and stomach, and the parietal layer lining the abdominal wall. Between these layers lies a tiny space filled with lubricating fluid, allowing organs to glide smoothly against each other and preventing friction. The Peritoneum also plays a role in absorbing nutrients and fighting infections, making it a crucial part of your internal ecosystem.
Did you know? The Peritoneum is the largest serous membrane in the human body, with a surface area roughly the size of a bed sheet! Keeping this important lining healthy through a balanced diet and regular exercise can contribute to overall digestive health and well-being.
Pleura
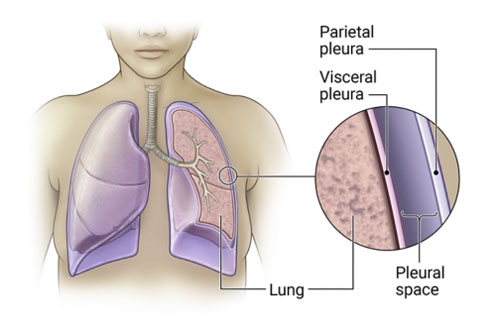
Enveloping the lungs are two thin membranes called the pleura. They provide lubrication and facilitate the smooth expansion and contraction of the lungs during breathing.
Prostate
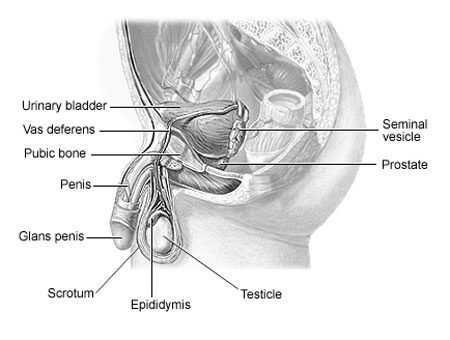
Exclusive to males, the prostate is a walnut-sized gland located beneath the bladder. It secretes a fluid that nourishes and protects sperm, playing a crucial role in the male reproductive system.
Pupil
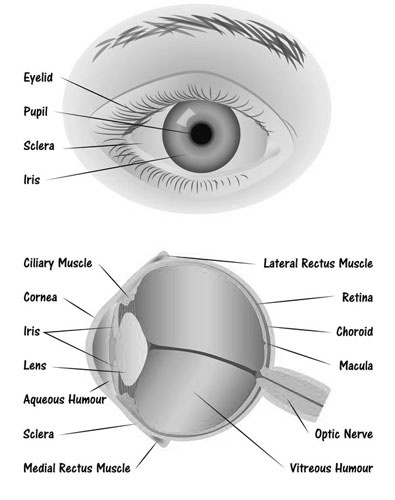
Central to the human eye’s anatomy is the pupil, the black, circular opening in the middle of the iris. It regulates the amount of light entering the eye, contracting in bright conditions and dilating in dimmer settings to optimize vision.
Pericardium
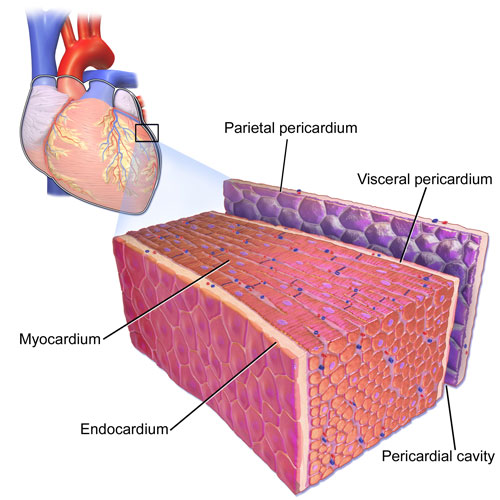
The heart, our rhythmic life pump, is encased in a double-walled sac called the pericardium. It provides protection, lubrication, and anchorage to the heart, ensuring its efficient function.
List of Human Body Parts Starting with P
| Palmar Arch | Pancreas | Papillary Muscles |
| Paranasal Sinuses | Parathyroid Glands | Pelvic Arteries |
| Pelvic Diaphragm | Pelvic Diaphragm, From Below | Pelvic Muscles |
| Pelvic Veins | Pelvis | Penis |
| Perineal Body | Perineal Body, Male | Perineal Membrane |
| Peritoneum | Phalanges | Pharyngeal Muscles |
| Pharynx | Phrenic Nerve | Phrenic Nerve, In Thorax |
| Pia Mater | Pineal Gland | Piriform Aperture |
| Piriformis Muscle | Pituitary Fossa | Pituitary Gland |
| Plantar Aponeurosis | Plantar Muscles | Plantar Nerve |
| Popliteal Artery | Posterior Cerebral Artery | Posterior Communicating Artery |
| Posterior Cranial Fossa | Posterior Longitudinal Ligament | Psoas Major Muscle |
| Pterygoid Muscles | Pulmonary Artery | Pulmonary Veins |
| Pericardium | Pupil | Prostate |
| Pleura | Plasma | Patella |
| Parietal Lobe |
Conclusion
The “P” segment in human anatomy offers a broad spectrum of organs and structures, underscoring the multifaceted nature of our body. From the depths of our brains to the tips of our fingers and toes, the components beginning with “P” illustrate the balance and harmony inherent in our design. This exploration fosters not just knowledge but a profound respect for the interplay of systems and structures that keep us alive and thriving. The journey through the vast corridors of human anatomy is enlightening, and with each discovery, we come to cherish the remarkable vessel that is the human body.
Human Body Parts That Start With
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W